Discrepancy between the in vitro and in vivo effects of murine mesenchymal stem cells on T-cell proliferation and collagen-induced arthritis
- PMID: 20175883
- PMCID: PMC2875665
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2939
Discrepancy between the in vitro and in vivo effects of murine mesenchymal stem cells on T-cell proliferation and collagen-induced arthritis
Abstract
Introduction: The goal of this study is to analyze the potential immunosuppressive properties of mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) on T cell proliferation and in collagen-induced arthritis (CIA). An additional aim is to investigate the role of interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) in these processes.
Methods: MSC were isolated from bone marrow of DBA/1 wild type and IFN-gamma receptor knock-out (IFN-gammaR KO) mice and expanded in vitro. Proliferation of anti-CD3-stimulated CD4+ T cells in the presence or absence of MSC was evaluated by thymidine incorporation. CIA was induced in DBA/1 mice and animals were treated with MSC by intravenous or intraperitoneal injections of wild type or IFN-gammaR KO MSC.
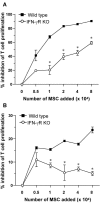
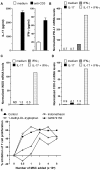
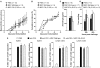
Results: Purity of enriched MSC cultures was evaluated by flow cytometry and their ability to differentiate into osteoblasts and adipocytes. In vitro, wild type MSC dose-dependently suppressed anti-CD3-induced T cell proliferation whereas IFN-gammaR KO MSC had a significantly lower inhibitory potential. A role for inducible nitric oxide (iNOS), programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), but not indoleamine 2,3-dioxigenase (IDO), in the T cell inhibition was demonstrated. In vivo, neither wild type nor IFN-gammaR KO MSC were able to reduce the severity of CIA or the humoral or cellular immune response toward collagen type II.
Conclusions: Whereas MSC inhibit anti-CD3-induced proliferation of T cells in vitro, an effect partially mediated by IFN-gamma, MSC do not influence in vivo T cell proliferation nor the disease course of CIA. Thus there is a clear discrepancy between the in vitro and in vivo effects of MSC on T cell proliferation and CIA.
Figures

Comment in
-
Mesenchymal stem cells in autoimmune diseases: hype or hope?Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(3):126. doi: 10.1186/ar3036. Epub 2010 Jun 18. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010. PMID: 20602812 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Defective CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cell functioning in collagen-induced arthritis: an important factor in pathogenesis, counter-regulated by endogenous IFN-gamma.Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7(2):R402-15. doi: 10.1186/ar1500. Epub 2005 Jan 28. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005. PMID: 15743488 Free PMC article.
-
Human embryonic stem cell-derived mesenchymal stromal cells ameliorate collagen-induced arthritis by inducing host-derived indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase.Arthritis Res Ther. 2016 Apr 1;18:77. doi: 10.1186/s13075-016-0979-0. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 27036118 Free PMC article.
-
Ameliorated course of glucose-6-phosphate isomerase (G6PI)-induced arthritis in IFN-γ receptor knockout mice exposes an arthritis-promoting role of IFN-γ.J Autoimmun. 2011 Mar;36(2):161-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2010.12.006. Epub 2011 Jan 22. J Autoimmun. 2011. PMID: 21262564
-
Collagen-induced arthritis as an animal model for rheumatoid arthritis: focus on interferon-γ.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011 Dec;31(12):917-26. doi: 10.1089/jir.2011.0056. Epub 2011 Sep 9. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011. PMID: 21905879 Review.
-
[The effect of interferon-gamma in collagen-induced arthritis in mice shows a mechanism of expanding Mac-1+ blood cells during its pathogenesis].Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 2005;67(2):125-37. Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 2005. PMID: 16089294 Review. Dutch.
Cited by
-
Immunomodulatory Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 20;11:1912. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01912. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32973792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic mismatch affects the immunosuppressive properties of mesenchymal stem cells in vitro and their ability to influence the course of collagen-induced arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2012 Jul 19;14(4):R167. doi: 10.1186/ar3916. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012. PMID: 22812502 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem cells in autoimmune diseases: hype or hope?Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(3):126. doi: 10.1186/ar3036. Epub 2010 Jun 18. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010. PMID: 20602812 Free PMC article.
-
A20 Restrains Thymic Regulatory T Cell Development.J Immunol. 2017 Oct 1;199(7):2356-2365. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1602102. Epub 2017 Aug 25. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28842469 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic application of mesenchymal stem cells in bone and joint diseases.Clin Exp Med. 2014 Feb;14(1):13-24. doi: 10.1007/s10238-012-0218-1. Epub 2012 Nov 3. Clin Exp Med. 2014. PMID: 23124706 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

