Renin-angiotensin system activation correlates with microvascular dysfunction in a prospective cohort study of clinical sepsis
- PMID: 20175923
- PMCID: PMC2875539
- DOI: 10.1186/cc8887
Renin-angiotensin system activation correlates with microvascular dysfunction in a prospective cohort study of clinical sepsis
Abstract
Introduction: Microvascular dysregulation characterized by hyporesponsive vessels and heterogeneous bloodflow is implicated in the pathogenesis of organ failure in sepsis. The renin-angiotensin system (RAS) affects the microvasculature, yet the relationships between RAS and organ injury in clinical sepsis remain unclear. We tested our hypothesis that systemic RAS mediators are associated with dysregulation of the microvasculature and with organ failure in clinical severe sepsis.
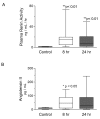
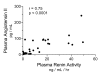
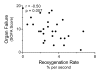
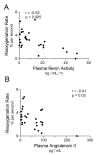
Methods: We studied 30 subjects with severe sepsis, and 10 healthy control subjects. Plasma was analyzed for plasma renin activity (PRA) and angiotensin II concentration (Ang II). Using near-infrared spectroscopy, we measured the rate of increase in the oxygen saturation of thenar microvascular hemoglobin after five minutes of induced forearm ischemia. In so doing, we assessed bulk microvascular hemoglobin influx to the tissue during reactive hyperemia. We studied all subjects 24 hours after the development of organ failure. We studied a subset of 12 subjects at an additional timepoint, eight hours after recognition of organ failure (early sepsis).
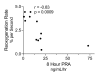
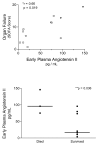
Results: After 24 hours of resuscitation to clinically-defined endpoints of preload and arterial pressure, Ang II and PRA were elevated in septic subjects and the degree of elevation correlated negatively with the rate of microvascular reoxygenation during reactive hyperemia. Early RAS mediators correlated with microvascular dysfunction. Early Ang II also correlated with the extent of organ failure realized during the first day of sepsis.
Conclusions: RAS is activated in clinical severe sepsis. Systemic RAS mediators correlate with measures of microvascular dysregulation and with organ failure.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impairments in microvascular reactivity are related to organ failure in human sepsis.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007 Aug;293(2):H1065-71. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.01237.2006. Epub 2007 May 4. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17483235
-
Association of Active Renin Content With Mortality in Critically Ill Patients: A Post hoc Analysis of the Vitamin C, Thiamine, and Steroids in Sepsis (VICTAS) Trial.Crit Care Med. 2024 Mar 1;52(3):441-451. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000006095. Epub 2023 Nov 10. Crit Care Med. 2024. PMID: 37947484 Free PMC article.
-
Stronger association of intact angiotensinogen with mortality than lactate or renin in critical illness: post-hoc analysis from the VICTAS trial.Crit Care. 2024 Oct 14;28(1):333. doi: 10.1186/s13054-024-05120-w. Crit Care. 2024. PMID: 39402593 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Modulation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in sepsis: a new therapeutic approach?Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2010 Jan;14(1):11-20. doi: 10.1517/14728220903460332. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2010. PMID: 20001206 Review.
-
The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone-system in sepsis and its clinical modulation with exogenous angiotensin II.Crit Care. 2024 Nov 26;28(1):389. doi: 10.1186/s13054-024-05123-7. Crit Care. 2024. PMID: 39593182 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pulmonary midkine inhibition ameliorates sepsis induced lung injury.J Transl Med. 2021 Feb 27;19(1):91. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-02755-z. J Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 33639987 Free PMC article.
-
Serum renin and major adverse kidney events in critically ill patients: a multicenter prospective study.Crit Care. 2021 Aug 14;25(1):294. doi: 10.1186/s13054-021-03725-z. Crit Care. 2021. PMID: 34391450 Free PMC article.
-
Acute toll-like receptor 4 activation impairs rat renal microvascular autoregulatory behaviour.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2017 Nov;221(3):204-220. doi: 10.1111/apha.12899. Epub 2017 Jun 27. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2017. PMID: 28544543 Free PMC article.
-
Multifunctional angiotensin converting enzyme 2, the SARS-CoV-2 entry receptor, and critical appraisal of its role in acute lung injury.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Apr;136:111193. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111193. Epub 2021 Jan 5. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33461019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Gene Polymorphism and Severe Lung Injury in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019.Am J Pathol. 2020 Oct;190(10):2013-2017. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2020.07.009. Epub 2020 Jul 29. Am J Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32735889 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ellis CG, Bateman RM, Sharpe MD, Sibbald WJ, Gill R. Effect of a maldistribution of microvascular blood flow on capillary O(2) extraction in sepsis. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2002;282:H156–164. - PubMed
-
- Tyml K, Yu J, McCormack DG. Capillary and arteriolar responses to local vasodilators are impaired in a rat model of sepsis. J Appl Physiol. 1998;84:837–844. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

