Neuroendocrinology of sexual plasticity in teleost fishes
- PMID: 20176046
- PMCID: PMC2885357
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2010.02.002
Neuroendocrinology of sexual plasticity in teleost fishes
Abstract
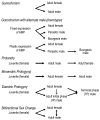
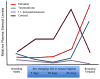
The study of sex differences has produced major insights into the organization of animal phenotypes and the regulatory mechanisms generating phenotypic variation from similar genetic templates. Teleost fishes display the greatest diversity of sexual expression among vertebrate animals. This diversity appears to arise from diversity in the timing of sex determination and less functional interdependence among the components of sexuality relative to tetrapod vertebrates. Teleost model systems therefore provide powerful models for understanding gonadal and non-gonadal influences on behavioral and physiological variation. This review addresses socially-controlled sex change and alternate male phenotypes in fishes. These sexual patterns are informative natural experiments that illustrate how variation in conserved neuroendocrine pathways can give rise to a wide range of reproductive adaptations. Key regulatory factors underlying sex change and alternative male phenotypes that have been identified to date include steroid hormones and the neuropeptides GnRH and arginine vasotocin, but genomic approaches are now implicating a diversity of other influences as well.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Estrogenic influences on agonistic behavior in teleost fishes.Horm Behav. 2024 May;161:105519. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2024.105519. Epub 2024 Mar 6. Horm Behav. 2024. PMID: 38452611 Review.
-
Serial adult sex change involves rapid and reversible changes in forebrain neurochemistry.Neuroreport. 1996 Nov 25;7(18):2945-9. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199611250-00029. Neuroreport. 1996. PMID: 9116216
-
Preoptic GnRH and AVT: axes for sexual plasticity in teleost fish.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1999 Nov;116(2):141-52. doi: 10.1006/gcen.1999.7357. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1999. PMID: 10562445 Review.
-
Social influences on the arginine vasotocin system are independent of gonads in a sex-changing fish.J Neurosci. 2003 May 15;23(10):4386-93. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-10-04386.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12764128 Free PMC article.
-
Social and neural modulation of sexual plasticity in teleost fish.Brain Behav Evol. 2001 May;57(5):293-300. doi: 10.1159/000047247. Brain Behav Evol. 2001. PMID: 11641565 Review.
Cited by
-
First neurotranscriptome of adults Tambaquis (Colossoma macropomum) with characterization and differential expression between males and females.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 7;14(1):3130. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-53734-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38326509 Free PMC article.
-
Seasonal expression of arginine vasotocin mRNA and its correlations to gonadal steroidogenic enzymes and sexually dimorphic coloration during sex reversal in the gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata).Fish Physiol Biochem. 2017 Jun;43(3):823-832. doi: 10.1007/s10695-017-0338-3. Epub 2017 Mar 18. Fish Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28315977
-
Novel behavioural assays reveal sex-specific behavioural syndromes in anemonefish.J Fish Biol. 2025 Jun;106(6):1845-1862. doi: 10.1111/jfb.16069. Epub 2025 Feb 18. J Fish Biol. 2025. PMID: 39963894 Free PMC article.
-
Stress and serial adult metamorphosis: multiple roles for the stress axis in socially regulated sex change.Front Neurosci. 2013 Nov 8;7:210. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2013.00210. eCollection 2013. Front Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24265604 Free PMC article.
-
Sex differences in the cognitive abilities of a sex-changing fish species Labroides dimidiatus.R Soc Open Sci. 2021 Jul 14;8(7):210239. doi: 10.1098/rsos.210239. eCollection 2021 Jul. R Soc Open Sci. 2021. PMID: 34295522 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alam MA, Bhandari RK, Kobayashi Y, Nakamura S, Soyano K, Nakamura M. Changes in androgen-producing cell size and circulating 11-ketotestosterone level during female-male sex change of honeycomb grouper Epinephelus merra. Molec Reprod Develop. 2006;73:206–214. - PubMed
-
- Arnold AP, Breedlove SM. Organizational and activational effects of sex steroids on brain and behavior - A reanalysis. Horm Behav. 1985;19:469–498. - PubMed
-
- Balment RJ, Lu W, Weybourne E, Warne JM. Arginine vasotocin a key hormone in fish physiology and behaviour: A review with insights from mammalian models. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2006;147:9–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

