Inhibitors of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase in cancer therapy
- PMID: 20176047
- PMCID: PMC2877630
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mam.2010.02.003
Inhibitors of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase in cancer therapy
Abstract
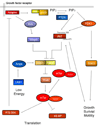
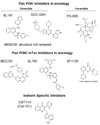
The phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) signaling pathway is implicated in multiple aspects of tumorigenesis and tumor maintenance, and recent years have seen significant efforts towards developing agents to inhibit the pathway. However, the development of such agents raises issues such as what specific member or members in the PI3K family should be inhibited to achieve maximal therapeutic benefit, and can specific inhibitors be developed with the necessary pharmacologic properties to allow them to proceed to clinical trials? The number of PI3K inhibitors has gone from a handful of archetypal inhibitors which largely determined how the pathway was initially defined through their inhibition of PI3K, but also due to their off target properties, to a much larger number of inhibitors of not only PI3K but also other members of the PI3K family. The question remains to be answered whether greater therapeutic efficacy will be obtained through the use of inhibitors with increased specificity, or through inhibitors that target a spectrum of targets within the pathway. This review will cover the development of agents targeting the pathway, and will discuss current issues surrounding the development of such agents.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway in cancer.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2009 Aug;8(8):627-44. doi: 10.1038/nrd2926. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2009. PMID: 19644473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PI3K and cancer: lessons, challenges and opportunities.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014 Feb;13(2):140-56. doi: 10.1038/nrd4204. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014. PMID: 24481312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
What a tangled web we weave: emerging resistance mechanisms to inhibition of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway.Cancer Discov. 2013 Dec;3(12):1345-54. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-13-0063. Epub 2013 Nov 21. Cancer Discov. 2013. PMID: 24265156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibiting the RAS-PI3K pathway in cancer therapy.Enzymes. 2013;34 Pt. B:107-36. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-420146-0.00005-6. Epub 2013 Nov 7. Enzymes. 2013. PMID: 25034102 Review.
-
New phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitors for cancer.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2011 Apr;20(4):507-18. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2011.562192. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2011. PMID: 21395485 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling in intestinal inflammation.J Signal Transduct. 2012;2012:358476. doi: 10.1155/2012/358476. Epub 2012 Apr 9. J Signal Transduct. 2012. PMID: 22570785 Free PMC article.
-
Target-based therapeutic matching in early-phase clinical trials in patients with advanced colorectal cancer and PIK3CA mutations.Mol Cancer Ther. 2013 Dec;12(12):2857-63. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0319-T. Epub 2013 Oct 3. Mol Cancer Ther. 2013. PMID: 24092809 Free PMC article.
-
Druggable binding sites in the multicomponent assemblies that characterise DNA double-strand-break repair through non-homologous end joining.Essays Biochem. 2020 Oct 26;64(5):791-806. doi: 10.1042/EBC20190092. Essays Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32579168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The PI3K inhibitor GDC-0941 displays promising in vitro and in vivo efficacy for targeted medulloblastoma therapy.Oncotarget. 2015 Jan 20;6(2):802-13. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2742. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25596739 Free PMC article.
-
PIK3CA kinase domain mutation identifies a subgroup of stage III colon cancer patients with poor prognosis.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2011 Dec;34(6):523-31. doi: 10.1007/s13402-011-0054-4. Epub 2011 Aug 10. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2011. PMID: 21830111
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources