Teolenn: an efficient and customizable workflow to design high-quality probes for microarray experiments
- PMID: 20176570
- PMCID: PMC2879536
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq110
Teolenn: an efficient and customizable workflow to design high-quality probes for microarray experiments
Abstract
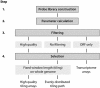
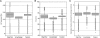
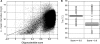
Despite the development of new high-throughput sequencing techniques, microarrays are still attractive tools to study small genome organisms, thanks to sample multiplexing and high-feature densities. However, the oligonucleotide design remains a delicate step for most users. A vast array of software is available to deal with this problem, but each program is developed with its own strategy, which makes the choice of the best solution difficult. Here we describe Teolenn, a universal probe design workflow developed with a flexible and customizable module organization allowing fixed or variable length oligonucleotide generation. In addition, our software is able to supply quality scores for each of the designed probes. In order to assess the relevance of these scores, we performed a real hybridization using a tiling array designed against the Trichoderma reesei fungus genome. We show that our scoring pipeline correlates with signal quality for 97.2% of all the designed probes, allowing for a posteriori comparisons between quality scores and signal intensities. This result is useful in discarding any bad scoring probes during the design step in order to get high-quality microarrays. Teolenn is available at http://transcriptome.ens.fr/teolenn/.
Figures


References
-
- Wold B, Myers RM. Sequence census methods for functional genomics. Nat. Meth. 2008;5:19–21. - PubMed
-
- Shendure J. The beginning of the end for microarrays? Nat. Meth. 2008;5:585–587. - PubMed
-
- Lipson D, Yakhini Z, Aumann Y. Optimization of probe coverage for high-resolution oligonucleotide aCGH. Bioinformatics. 2007;23:e77–e83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

