Entry of Neisseria meningitidis into mammalian cells requires the Src family protein tyrosine kinases
- PMID: 20176789
- PMCID: PMC2863495
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01267-09
Entry of Neisseria meningitidis into mammalian cells requires the Src family protein tyrosine kinases
Abstract
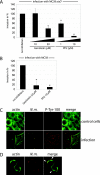
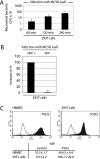
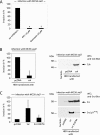
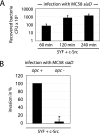
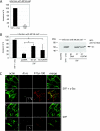
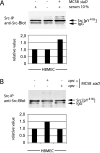
Neisseria meningitidis, the causative agent of meningitis and septicemia, is able to attach to and invade a variety of cell types. In a previous study we showed that entry of N. meningitidis into human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMEC) is mediated by fibronectin bound to the outer membrane protein Opc, which forms a molecular bridge to alpha 5 beta 1-integrins. This interaction results in cytoskeletal remodeling and uptake of the bacteria. In this study we identified and characterized the intracellular signals involved in integrin-initiated uptake of N. meningitidis. We determined that the Src protein tyrosine kinases (PTKs) are activated in response to contact with N. meningitidis. Inhibition of Src PTK activity by the general tyrosine kinase inhibitor genistein and the specific Src inhibitor PP2 reduced Opc-mediated invasion of HBMEC and human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293T cells up to 90%. Moreover, overexpression of the cellular Src antagonist C-terminal Src kinase (CSK) also significantly reduced N. meningitidis invasion. Src PTK-deficient fibroblasts were impaired in the ability to internalize N. meningitidis and showed reduced phosphorylation of the cytoskeleton and decreased development of stress fibers. These data indicate that the Src family PTKs, particularly the Src protein, along with other proteins, are important signal proteins that are responsible for the transfer of signals from activated integrins to the cytoskeleton and thus mediate the endocytosis of N. meningitidis into brain endothelial cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling in the interaction of Neisseria meningitidis with endothelial cells.Infect Immun. 2014 Mar;82(3):1243-55. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01346-13. Epub 2013 Dec 30. Infect Immun. 2014. PMID: 24379285 Free PMC article.
-
Cell invasion by Neisseria meningitidis requires a functional interplay between the focal adhesion kinase, Src and cortactin.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e39613. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039613. Epub 2012 Jun 29. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22768099 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of Neisseria meningitidis with human brain microvascular endothelial cells: role of MAP- and tyrosine kinases in invasion and inflammatory cytokine release.Cell Microbiol. 2004 Dec;6(12):1153-66. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2004.00422.x. Cell Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15527495
-
Neisseria meningitidis Opc invasin binds to the sulphated tyrosines of activated vitronectin to attach to and invade human brain endothelial cells.PLoS Pathog. 2010 May 20;6(5):e1000911. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000911. PLoS Pathog. 2010. PMID: 20502634 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms involved in the interaction of Neisseria meningitidis with cells of the human blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier.Pathog Dis. 2017 Mar 1;75(2). doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftx023. Pathog Dis. 2017. PMID: 28334198 Review.
Cited by
-
The Host-Pathogen Interactions and Epicellular Lifestyle of Neisseria meningitidis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Apr 22;12:862935. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.862935. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35531336 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling in the interaction of Neisseria meningitidis with endothelial cells.Infect Immun. 2014 Mar;82(3):1243-55. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01346-13. Epub 2013 Dec 30. Infect Immun. 2014. PMID: 24379285 Free PMC article.
-
The phosphoproteome of choroid plexus epithelial cells following infection with Neisseria meningitidis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Mar 31;13:1113528. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1113528. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37065199 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingosine kinase 1/S1P receptor signaling axis is essential for cellular uptake of Neisseria meningitidis in brain endothelial cells.PLoS Pathog. 2023 Nov 30;19(11):e1011842. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011842. eCollection 2023 Nov. PLoS Pathog. 2023. PMID: 38033162 Free PMC article.
-
Differential activation of acid sphingomyelinase and ceramide release determines invasiveness of Neisseria meningitidis into brain endothelial cells.PLoS Pathog. 2014 Jun 12;10(6):e1004160. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004160. eCollection 2014 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 24945304 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agerer, F., A. Michel, K. Ohlsen, and C. R. Hauck. 2003. Integrin-mediated invasion of Staphylococcus aureus into human cells requires Src family protein-tyrosine kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 278:42524-42531. - PubMed
-
- Agerer, F., S. Waeckerle, and C. R. Hauck. 2004. Microscopic quantification of bacterial invasion by a novel antibody-independent staining method. J. Microbiol. Methods 59:23-32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

