CCR7 deficiency leads to leukocyte activation and increased clearance in response to pulmonary Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection
- PMID: 20176793
- PMCID: PMC2863523
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00962-09
CCR7 deficiency leads to leukocyte activation and increased clearance in response to pulmonary Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection
Abstract
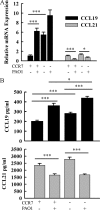
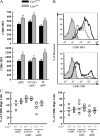
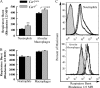
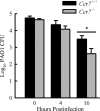
CCR7 is a chemokine receptor expressed on the surfaces of T cells, B cells, and mature dendritic cells that controls cell migration in response to the cognate ligands CCL19 and CCL21. CCR7 is critical for the generation of an adaptive T cell response. However, the roles of CCR7 in the host defense against pulmonary infection and innate immunity are not well understood. We investigated the role of CCR7 in the host defense against acute pulmonary infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. We intranasally infected C57BL/6 mice with P. aeruginosa and characterized the expression of CCR7 ligands and the surface expression of CCR7 on pulmonary leukocytes. In response to infection, expression of CCL19 and expression of CCL21 were oppositely regulated, and myeloid dendritic cells upregulated CCR7 expression. We further examined the effects of CCR7 deficiency on the inflammatory response to P. aeruginosa infection. We infected Ccr7(-/-) and wild-type mice with P. aeruginosa and characterized the accumulation of pulmonary leukocytes, production of proinflammatory mediators, neutrophil activation, and bacterial clearance. CCR7 deficiency led to an accumulation of myeloid dendritic cells and T cells in the lung in response to infection. CCR7 deficiency resulted in higher expression of CD80 and CD86 on dendritic cells; increased production of interleukin-12/23p40 (IL-12/23p40), gamma interferon (IFN-gamma), and IL-1 alpha; increased neutrophil respiratory burst; and, ultimately, increased clearance of acute P. aeruginosa infection. In conclusion, our results suggest that CCR7 deficiency results in a heightened proinflammatory environment in response to acute pulmonary P. aeruginosa infection and contributes to more efficient clearance.
Figures
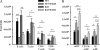
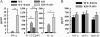
Similar articles
-
CCR7-dependent immunity during acute Toxoplasma gondii infection.Infect Immun. 2010 May;78(5):2257-63. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01314-09. Epub 2010 Mar 1. Infect Immun. 2010. PMID: 20194594 Free PMC article.
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 4 (STAT4), but not IL-12 contributes to Pseudomonas aeruginosa-induced lung inflammation in mice.Immunobiology. 2008;213(6):469-79. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2007.11.007. Epub 2008 Jan 2. Immunobiology. 2008. PMID: 18514749
-
Interleukin-18 impairs the pulmonary host response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Infect Immun. 2003 Apr;71(4):1630-4. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.4.1630-1634.2003. Infect Immun. 2003. PMID: 12654774 Free PMC article.
-
Common and biased signaling pathways of the chemokine receptor CCR7 elicited by its ligands CCL19 and CCL21 in leukocytes.J Leukoc Biol. 2016 Jun;99(6):869-82. doi: 10.1189/jlb.2MR0815-380R. Epub 2016 Jan 4. J Leukoc Biol. 2016. PMID: 26729814 Review.
-
A myriad of functions and complex regulation of the CCR7/CCL19/CCL21 chemokine axis in the adaptive immune system.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013 Jun;24(3):269-83. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2013.03.001. Epub 2013 Apr 12. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013. PMID: 23587803 Review.
Cited by
-
Immune and Stroma Related Genes in Breast Cancer: A Comprehensive Analysis of Tumor Microenvironment Based on the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) Database.Front Med (Lausanne). 2020 Mar 5;7:64. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.00064. eCollection 2020. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 32195260 Free PMC article.
-
Blockade of Interplay between IL-17A and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Attenuates LPS-Induced Lung Injury.Theranostics. 2015 Oct 7;5(12):1343-62. doi: 10.7150/thno.11685. eCollection 2015. Theranostics. 2015. PMID: 26516372 Free PMC article.
-
The B lymphocyte differentiation factor (BAFF) is expressed in the airways of children with CF and in lungs of mice infected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa.PLoS One. 2014 May 21;9(5):e95892. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095892. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24847941 Free PMC article.
-
Computational identification of key genetic drivers in COPD: A first step towards uncovering candidate biomarkers in smokers.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2025 Aug 1;43:102193. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2025.102193. eCollection 2025 Sep. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2025. PMID: 40800604 Free PMC article.
-
High-dimensional phenotyping of the peripheral immune response in community-acquired pneumonia.Front Immunol. 2023 Nov 24;14:1260283. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1260283. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38077404 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beaty, S. R., C. E. Rose, Jr., and S.-S. J. Sung. 2007. Diverse and potent chemokine production by lung CD11bhigh dendritic cells in homeostasis and in allergic lung inflammation. J. Immunol. 178:1882-1895. - PubMed
-
- Bromley, S. K., S. Y. Thomas, and A. D. Luster. 2005. Chemokine receptor CCR7 guides T cell exit from peripheral tissues and entry into afferent lymphatics. Nat. Immunol. 6:895-901. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

