Bleomycin and IL-1beta-mediated pulmonary fibrosis is IL-17A dependent
- PMID: 20176803
- PMCID: PMC2839145
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20092121
Bleomycin and IL-1beta-mediated pulmonary fibrosis is IL-17A dependent
Abstract
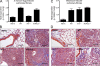
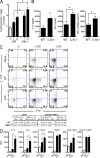
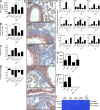
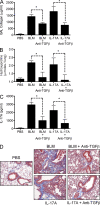
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a destructive inflammatory disease with limited therapeutic options. To better understand the inflammatory responses that precede and concur with collagen deposition, we used three models of pulmonary fibrosis and identify a critical mechanistic role for IL-17A. After exposure to bleomycin (BLM), but not Schistosoma mansoni eggs, IL-17A produced by CD4(+) and gammadelta(+) T cells induced significant neutrophilia and pulmonary fibrosis. Studies conducted with C57BL/6 il17a(-/-) mice confirmed an essential role for IL-17A. Mechanistically, using ifngamma(-/-), il10(-/-), il10(-/-)il12p40(-/-), and il10(-/-)il17a(-/-) mice and TGF-beta blockade, we demonstrate that IL-17A-driven fibrosis is suppressed by IL-10 and facilitated by IFN-gamma and IL-12/23p40. BLM-induced IL-17A production was also TGF-beta dependent, and recombinant IL-17A-mediated fibrosis required TGF-beta, suggesting cooperative roles for IL-17A and TGF-beta in the development of fibrosis. Finally, we show that fibrosis induced by IL-1beta, which mimics BLM-induced fibrosis, is also highly dependent on IL-17A. IL-17A and IL-1beta were also increased in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of patients with IPF. Together, these studies identify a critical role for IL-17A in fibrosis, illustrating the potential utility of targeting IL-17A in the treatment of drug and inflammation-induced fibrosis.
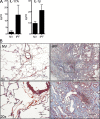
Figures




References
-
- Albanesi C., Cavani A., Girolomoni G. 1999. IL-17 is produced by nickel-specific T lymphocytes and regulates ICAM-1 expression and chemokine production in human keratinocytes: synergistic or antagonist effects with IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha. J. Immunol. 162:494–502 - PubMed
-
- Andoh A., Takaya H., Makino J., Sato H., Bamba S., Araki Y., Hata K., Shimada M., Okuno T., Fujiyama Y., Bamba T. 2001. Cooperation of interleukin-17 and interferon-gamma on chemokine secretion in human fetal intestinal epithelial cells. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 125:56–63 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2001.01588.x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arai T., Abe K., Matsuoka H., Yoshida M., Mori M., Goya S., Kida H., Nishino K., Osaki T., Tachibana I., et al. 2000. Introduction of the interleukin-10 gene into mice inhibited bleomycin-induced lung injury in vivo. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 278:L914–L922 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

