Anchorage of VEGF to the extracellular matrix conveys differential signaling responses to endothelial cells
- PMID: 20176926
- PMCID: PMC2828913
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200906044
Anchorage of VEGF to the extracellular matrix conveys differential signaling responses to endothelial cells
Abstract
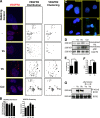
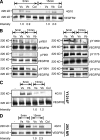
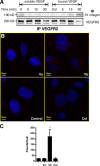
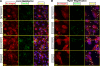
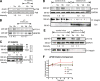
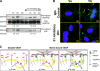
VEGF can be secreted in multiple isoforms with variable affinity for extracellular proteins and different abilities to induce vascular morphogenesis, but the molecular mechanisms behind these effects remain unclear. Here, we show molecular distinctions between signaling initiated from soluble versus matrix-bound VEGF, which mediates a sustained level of VEGFR2 internalization and clustering. Exposure of endothelial cells to matrix-bound VEGF elicits prolonged activation of VEGFR2 with differential phosphorylation of Y1214, and extended activation kinetics of p38. These events require association of VEGFR2 with beta1 integrins. Matrix-bound VEGF also promotes reciprocal responses on beta1 integrin by inducing its association with focal adhesions; a response that is absent upon exposure to soluble VEGF. Inactivation of beta1 integrin blocks the prolonged phosphorylation of Y1214 and consequent activation of p38. Combined, these results indicate that when in the context of extracellular matrix, activation of VEGFR2 is distinct from that of soluble VEGF in terms of recruitment of receptor partners, phosphorylation kinetics, and activation of downstream effectors.
Figures



References
-
- Anderson S.M., Chen T.T., Iruela-Arispe M.L., Segura T. 2009. The phosphorylation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (VEGFR-2) by engineered surfaces with electrostatically or covalently immobilized VEGF. Biomaterials. 30:4618–4628 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.05.030 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ashikari-Hada S., Habuchi H., Kariya Y., Kimata K. 2005. Heparin regulates vascular endothelial growth factor165-dependent mitogenic activity, tube formation, and its receptor phosphorylation of human endothelial cells. Comparison of the effects of heparin and modified heparins. J. Biol. Chem. 280:31508–31515 10.1074/jbc.M414581200 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bates D.O., Cui T.G., Doughty J.M., Winkler M., Sugiono M., Shields J.D., Peat D., Gillatt D., Harper S.J. 2002. VEGF165b, an inhibitory splice variant of vascular endothelial growth factor, is down-regulated in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 62:4123–4131 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

