Nebivolol improves diastolic dysfunction and myocardial remodeling through reductions in oxidative stress in the Zucker obese rat
- PMID: 20176997
- PMCID: PMC2841702
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.109.145136
Nebivolol improves diastolic dysfunction and myocardial remodeling through reductions in oxidative stress in the Zucker obese rat
Abstract
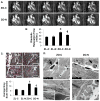
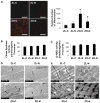
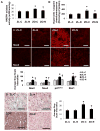
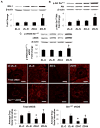
Insulin resistance is associated with obesity and may be accompanied by left ventricular diastolic dysfunction and myocardial remodeling. Decreased insulin metabolic signaling and increased oxidative stress may promote these maladaptive changes. In this context, the beta-blocker nebivolol has been reported to improve insulin sensitivity, increase endothelial NO synthase activity, and reduce NADPH oxidase-induced superoxide generation. We hypothesized that nebivolol would attenuate diastolic dysfunction and myocardial remodeling by blunting myocardial oxidant stress and promoting insulin metabolic signaling in a rodent model of obesity, insulin resistance, and hypertension. Six-week-old male Zucker obese and age-matched Zucker lean rats were treated with nebivolol (10 mg x kg(-) x day(-1)) for 21 days, and myocardial function was assessed by cine MRI. Compared with untreated Zucker lean rats, untreated Zucker obese rats exhibited prolonged diastolic relaxation time (27.7+/-2.5 versus 40.9+/-2.0 ms; P<0.05) and reduced initial diastolic filling rate (6.2+/-0.5 versus 2.8+/-0.6 microL/ms; P<0.05) in conjunction with increased homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (7+/-2 versus 95+/-21; P<0.05), interstitial and pericapillary fibrosis, abnormal cardiomyocyte histoarchitecture, 3-nitrotyrosine, and NADPH oxidase-dependent superoxide. Nebivolol improved diastolic relaxation (32.8+/-0.7 ms; P<0.05 versus untreated Zucker obese), reduced fibrosis, and remodeling in Zucker obese rats, in concert with reductions in nitrotyrosine, NADPH oxidase-dependent superoxide, and improvements in the insulin metabolic signaling, endothelial NO synthase activation, and weight gain (381+/-7 versus 338+/-14 g; P<0.05). Results support the hypothesis that nebivolol reduces myocardial structural maladaptive changes and improves diastolic relaxation in concert with improvements in insulin sensitivity and endothelial NO synthase activation, concomitantly with reductions in oxidative stress.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nebivolol improves diastolic dysfunction and myocardial remodeling through reductions in oxidative stress in the transgenic (mRen2) rat.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012 Jun 1;302(11):H2341-51. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.01126.2011. Epub 2012 Mar 23. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22447938 Free PMC article.
-
Nebivolol improves insulin sensitivity in the TGR(Ren2)27 rat.Metabolism. 2011 Dec;60(12):1757-66. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2011.04.009. Epub 2011 Jun 2. Metabolism. 2011. PMID: 21640361 Free PMC article.
-
Nebivolol attenuates redox-sensitive glomerular and tubular mediated proteinuria in obese rats.Endocrinology. 2011 Feb;152(2):659-68. doi: 10.1210/en.2010-1038. Epub 2010 Dec 22. Endocrinology. 2011. PMID: 21177830 Free PMC article.
-
Nebivolol: a highly selective beta1-adrenergic receptor blocker that causes vasodilation by increasing nitric oxide.Cardiovasc Ther. 2008 Fall;26(3):189-202. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5922.2008.00054.x. Cardiovasc Ther. 2008. PMID: 18786089 Review.
-
Nebivolol: impact on cardiac and endothelial function and clinical utility.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2012;8:151-60. doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S20669. Epub 2012 Mar 13. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2012. PMID: 22454559 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Overweight and Obesity in the Cardiorenal Syndrome.Cardiorenal Med. 2011;1(1):5-12. doi: 10.1159/000322822. Epub 2011 Jan 17. Cardiorenal Med. 2011. PMID: 22258461 Free PMC article.
-
Obesity-related alterations in cardiac lipid profile and nondipping blood pressure pattern during transition to diastolic dysfunction in male db/db mice.Endocrinology. 2013 Jan;154(1):159-71. doi: 10.1210/en.2012-1835. Epub 2012 Nov 9. Endocrinology. 2013. PMID: 23142808 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of eNOS Partially Blunts the Beneficial Effects of Nebivolol on Angiotensin II-Induced Signaling in H9c2 Cardiomyoblasts.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022 May 10;44(5):2139-2152. doi: 10.3390/cimb44050144. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35678673 Free PMC article.
-
Short-and long-term administration of imeglimin counters cardiorenal dysfunction in a rat model of metabolic syndrome.Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2020 Apr 16;3(3):e00128. doi: 10.1002/edm2.128. eCollection 2020 Jul. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2020. PMID: 32704553 Free PMC article.
-
Nebivolol Prevents Up-Regulation of Nox2/NADPH Oxidase and Lipoperoxidation in the Early Stages of Ethanol-Induced Cardiac Toxicity.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2021 Mar;21(3):224-235. doi: 10.1007/s12012-020-09614-1. Epub 2020 Oct 16. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33067693
References
-
- Alpert MA, Lambert CR, Terry BE, Cohen MV, Mukerji V, Massey CV, Hashimi MW, Panayiotou H. Interrelationship of left ventricular mass, systolic function and diastolic filling in normotensive morbidly obese patients. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1995;19:550–557. - PubMed
-
- Lauer MS, Anderson KM, Kannel WB, Levy D. The impact of obesity on left ventricular mass and geometry. The Framingham Heart Study. JAMA. 1991;266:231–236. - PubMed
-
- Wei Y, Whaley-Connell AT, Chen K, Habibi J, Uptergrove GM, Clark SE, Stump CS, Ferrario CM, Sowers JR. NADPH oxidase contributes to vascular inflammation, insulin resistance, and remodeling in the transgenic (mRen2) rat. Hypertension. 2007;50:384–391. - PubMed
-
- Munzel T, Daiber A, Ullrich V, Mulsch A. Vascular consequences of endothelial nitric oxide synthase uncoupling for the activity and expression of the soluble guanylyl cyclase and the cGMP-dependent protein kinase. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005;25:1551–1557. - PubMed
-
- Cai H, Harrison DG. Endothelial dysfunction in cardiovascular diseases: the role of oxidant stress. Circ Res. 2000;87:840–844. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

