Inhibition of Na+-taurocholate Co-transporting polypeptide-mediated bile acid transport by cholestatic sulfated progesterone metabolites
- PMID: 20177056
- PMCID: PMC2878045
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.072140
Inhibition of Na+-taurocholate Co-transporting polypeptide-mediated bile acid transport by cholestatic sulfated progesterone metabolites
Abstract
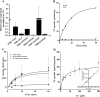
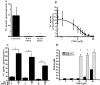
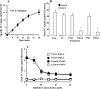
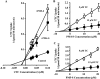
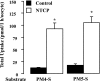
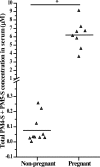
Sulfated progesterone metabolite (P4-S) levels are raised in normal pregnancy and elevated further in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP), a bile acid-liver disorder of pregnancy. ICP can be complicated by preterm labor and intrauterine death. The impact of P4-S on bile acid uptake was studied using two experimental models of hepatic uptake of bile acids, namely cultured primary human hepatocytes (PHH) and Na(+)-taurocholate co-transporting polypeptide (NTCP)-expressing Xenopus laevis oocytes. Two P4-S compounds, allopregnanolone-sulfate (PM4-S) and epiallopregnanolone-sulfate (PM5-S), reduced [(3)H]taurocholate (TC) uptake in a dose-dependent manner in PHH, with both Na(+)-dependent and -independent bile acid uptake systems significantly inhibited. PM5-S-mediated inhibition of TC uptake could be reversed by increasing the TC concentration against a fixed PM5-S dose indicating competitive inhibition. Experiments using NTCP-expressing Xenopus oocytes confirmed that PM4-S/PM5-S are capable of competitively inhibiting NTCP-mediated uptake of [(3)H]TC. Total serum PM4-S + PM5-S levels were measured in non-pregnant and third trimester pregnant women using liquid chromatography-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry and were increased in pregnant women, at levels capable of inhibiting TC uptake. In conclusion, pregnancy levels of P4-S can inhibit Na(+)-dependent and -independent influx of taurocholate in PHH and cause competitive inhibition of NTCP-mediated uptake of taurocholate in Xenopus oocytes.
Figures
References
-
- Pascual M. J., Serrano M. A., El-Mir M. Y., Macias R. I., Jiménez F., Marin J. J. (2002) Clin. Sci. 102, 587–593 - PubMed
-
- Castaño G., Lucangioli S., Sookoian S., Mesquida M., Lemberg A., Di Scala M., Franchi P., Carducci C., Tripodi V. (2006) Clin. Sci. 110, 459–465 - PubMed
-
- Glantz A., Marschall H. U., Mattsson L. A. (2004) Hepatology 40, 467–474 - PubMed
-
- Williamson C., Hems L. M., Goulis D. G., Walker I., Chambers J., Donaldson O., Swiet M., Johnston D. G. (2004) BJOG 111, 676–681 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

