Ubiquitination of PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homolog) inhibits phosphatase activity and is enhanced by membrane targeting and hyperosmotic stress
- PMID: 20177066
- PMCID: PMC2857106
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.072280
Ubiquitination of PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homolog) inhibits phosphatase activity and is enhanced by membrane targeting and hyperosmotic stress
Abstract
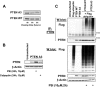
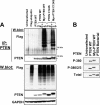
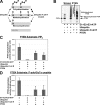
The PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homolog) tumor suppressor is a phosphatase that inhibits phosphoinositide 3-kinase-dependent signaling by metabolizing the phosphoinositide lipid phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate (PtdInsP(3)) at the plasma membrane. PTEN can be mono- or polyubiquitinated, and this appears to control its nuclear localization and stability, respectively. Although PTEN phosphorylation at a cluster of C-terminal serine and threonine residues has been shown to stabilize the protein and inhibit polyubiquitination and plasma membrane localization, details of the regulation of ubiquitination are unclear. Here, we show that plasma membrane targeting of PTEN greatly enhances PTEN ubiquitination and that phosphorylation of PTEN in vitro does not affect subsequent ubiquitination. These data suggest that C-terminal phosphorylation indirectly regulates ubiquitination by controlling membrane localization. We also show that either mono- or polyubiquitination in vitro greatly reduces PTEN phosphatase activity. Finally, we show that hyperosmotic stress increases both PTEN ubiquitination and cellular PtdInsP(3) levels well before a reduction in PTEN protein levels is observed. Both PTEN ubiquitination and elevated PtdInsP(3) levels were reduced within 10 min after removal of the hyperosmotic stress. Our data indicate that ubiquitination may represent a regulated mechanism of direct reversible control over the PTEN enzyme.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Controlling PTEN (Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog) Stability: A DOMINANT ROLE FOR LYSINE 66.J Biol Chem. 2016 Aug 26;291(35):18465-73. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.727750. Epub 2016 Jul 12. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27405757 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of phosphoinositide metabolism, Akt phosphorylation, and glucose transport by PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10) in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.Mol Endocrinol. 2001 Aug;15(8):1411-22. doi: 10.1210/mend.15.8.0684. Mol Endocrinol. 2001. PMID: 11463863
-
Evidence that SHIP-1 contributes to phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate metabolism in T lymphocytes and can regulate novel phosphoinositide 3-kinase effectors.J Immunol. 2002 Nov 15;169(10):5441-50. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.10.5441. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12421919
-
Understanding PTEN regulation: PIP2, polarity and protein stability.Oncogene. 2008 Sep 18;27(41):5464-76. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.243. Oncogene. 2008. PMID: 18794881 Review.
-
The regulation of cell migration by PTEN.Biochem Soc Trans. 2005 Dec;33(Pt 6):1507-8. doi: 10.1042/BST0331507. Biochem Soc Trans. 2005. PMID: 16246156 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent advances in PTEN signalling axes in cancer.Fac Rev. 2020 Dec 23;9:31. doi: 10.12703/r/9-31. eCollection 2020. Fac Rev. 2020. PMID: 33659963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear PTEN's Functions in Suppressing Tumorigenesis: Implications for Rare Cancers.Biomolecules. 2023 Jan 30;13(2):259. doi: 10.3390/biom13020259. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 36830628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphoinositides: tiny lipids with giant impact on cell regulation.Physiol Rev. 2013 Jul;93(3):1019-137. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00028.2012. Physiol Rev. 2013. PMID: 23899561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fluctuations in AKT and PTEN Activity Are Linked by the E3 Ubiquitin Ligase cCBL.Cells. 2021 Oct 20;10(11):2803. doi: 10.3390/cells10112803. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831026 Free PMC article.
-
PPIP5K1 modulates ligand competition between diphosphoinositol polyphosphates and PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 for polyphosphoinositide-binding domains.Biochem J. 2013 Aug 1;453(3):413-26. doi: 10.1042/BJ20121528. Biochem J. 2013. PMID: 23682967 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

