Phosphorylation of TRPC6 channels at Thr69 is required for anti-hypertrophic effects of phosphodiesterase 5 inhibition
- PMID: 20177073
- PMCID: PMC2857061
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.074104
Phosphorylation of TRPC6 channels at Thr69 is required for anti-hypertrophic effects of phosphodiesterase 5 inhibition
Abstract
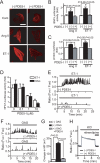
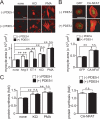
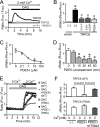
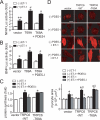
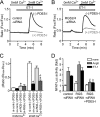
Activation of Ca(2+) signaling induced by receptor stimulation and mechanical stress plays a critical role in the development of cardiac hypertrophy. A canonical transient receptor potential protein subfamily member, TRPC6, which is activated by diacylglycerol and mechanical stretch, works as an upstream regulator of the Ca(2+) signaling pathway. Although activation of protein kinase G (PKG) inhibits TRPC6 channel activity and cardiac hypertrophy, respectively, it is unclear whether PKG suppresses cardiac hypertrophy through inhibition of TRPC6. Here, we show that inhibition of cGMP-selective PDE5 (phosphodiesterase 5) suppresses endothelin-1-, diacylglycerol analog-, and mechanical stretch-induced hypertrophy through inhibition of Ca(2+) influx in rat neonatal cardiomyocytes. Inhibition of PDE5 suppressed the increase in frequency of Ca(2+) spikes induced by agonists or mechanical stretch. However, PDE5 inhibition did not suppress the hypertrophic responses induced by high KCl or the activation of protein kinase C, suggesting that PDE5 inhibition suppresses Ca(2+) influx itself or molecule(s) upstream of Ca(2+) influx. PKG activated by PDE5 inhibition phosphorylated TRPC6 proteins at Thr(69) and prevented TRPC6-mediated Ca(2+) influx. Substitution of Ala for Thr(69) in TRPC6 abolished the anti-hypertrophic effects of PDE5 inhibition. In addition, chronic PDE5 inhibition by oral sildenafil treatment actually induced TRPC6 phosphorylation in mouse hearts. Knockdown of RGS2 (regulator of G protein signaling 2) and RGS4, both of which are activated by PKG to reduce G alpha(q)-mediated signaling, did not affect the suppression of receptor-activated Ca(2+) influx by PDE5 inhibition. These results suggest that phosphorylation and functional suppression of TRPC6 underlie prevention of pathological hypertrophy by PDE5 inhibition.
Figures
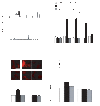

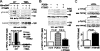

Similar articles
-
[Regulation of cardiovascular functions by the phosphorylation of TRPC channels].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2010 Nov;130(11):1427-33. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.130.1427. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2010. PMID: 21048399 Review. Japanese.
-
Cyclic GMP/PKG-dependent inhibition of TRPC6 channel activity and expression negatively regulates cardiomyocyte NFAT activation Novel mechanism of cardiac stress modulation by PDE5 inhibition.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2010 Apr;48(4):713-24. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2009.11.015. Epub 2009 Dec 1. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2010. PMID: 19961855 Free PMC article.
-
Regulator of G protein signaling 2 mediates cardiac compensation to pressure overload and antihypertrophic effects of PDE5 inhibition in mice.J Clin Invest. 2009 Feb;119(2):408-20. doi: 10.1172/JCI35620. Epub 2009 Jan 5. J Clin Invest. 2009. PMID: 19127022 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic inhibition of cGMP-specific phosphodiesterase 5 suppresses endoplasmic reticulum stress in heart failure.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Dec;170(7):1396-409. doi: 10.1111/bph.12346. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24032459 Free PMC article.
-
[Mechanism of cardiac hypertrophy via diacylglycerol-sensitive TRPC channels].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2010 Mar;130(3):295-302. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.130.295. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2010. PMID: 20190513 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Cardiac Phosphodiesterases and Their Modulation for Treating Heart Disease.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2017;243:249-269. doi: 10.1007/164_2016_82. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27787716 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proline-dependent and basophilic kinases phosphorylate human TRPC6 at serine 14 to control channel activity through increased membrane expression.FASEB J. 2018 Jan;32(1):208-219. doi: 10.1096/fj.201700309R. Epub 2017 Sep 6. FASEB J. 2018. PMID: 28877958 Free PMC article.
-
The Pattern of mRNA Expression Is Changed in Sinoatrial Node from Goto-Kakizaki Type 2 Diabetic Rat Heart.J Diabetes Res. 2018 Sep 2;2018:8454078. doi: 10.1155/2018/8454078. eCollection 2018. J Diabetes Res. 2018. PMID: 30246030 Free PMC article.
-
The role of mechanical tension on lipid raft dependent PDGF-induced TRPC6 activation.Biomaterials. 2014 Mar;35(9):2868-77. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.12.030. Epub 2014 Jan 4. Biomaterials. 2014. PMID: 24397990 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic Analysis of Myocardia Containing the Obscurin R4344Q Mutation Linked to Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy.Front Physiol. 2020 May 18;11:478. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00478. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32528308 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

