Automated medical image segmentation techniques
- PMID: 20177565
- PMCID: PMC2825001
- DOI: 10.4103/0971-6203.58777
Automated medical image segmentation techniques
Abstract
Accurate segmentation of medical images is a key step in contouring during radiotherapy planning. Computed topography (CT) and Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging are the most widely used radiographic techniques in diagnosis, clinical studies and treatment planning. This review provides details of automated segmentation methods, specifically discussed in the context of CT and MR images. The motive is to discuss the problems encountered in segmentation of CT and MR images, and the relative merits and limitations of methods currently available for segmentation of medical images.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence techniques; computed tomography; magnetic resonance imaging; medical images artifacts; segmentation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

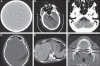
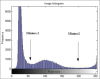
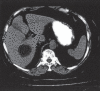
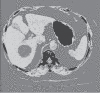

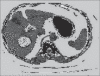
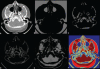
References
-
- Withey DJ, Koles ZJ. Three generations of medical image segmentation: Methods and available software. Int J Bioelectromag. 2007;9:67–8.
-
- Prince JL, Links JM. Medical imaging signals and system. Pearson Education. 2006.
-
- Macovski A. Medical imaging systems. Prentice-Hall; 1983.
-
- Popilock R, Sandrasagaren K, Harris L, Kaser KA. CT artifact recognition for the nuclear technologist. J Nucl Med Technol. 2008;36:79–81. - PubMed
-
- Li H, Deklerck R, Cuyper BD, Hermanus A, Nyssen E, Cornelis J. Object recognition in brain CT-scans: Knowledge based fusion of data from multiple feature extractors. IEEE T Med Imaging. 1995;14:212–29. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

