Angiogenesis, neurogenesis and brain recovery of function following injury
- PMID: 20178043
- PMCID: PMC2836170
Angiogenesis, neurogenesis and brain recovery of function following injury
Abstract
Stroke and traumatic brain injury (TBI) are major causes of mortality and morbidity worldwide. Unfortunately, almost all phase III clinical trials of neuroprotective agents for stroke and TBI have demonstrated no benefit, raising concerns regarding the use of neuroprotective strategies alone as therapy for acute brain injuries. Therefore, a compelling need exists to develop treatments that promote both the repair and regeneration of injured brain tissue, and functional recovery. Recent data suggest that strategies to enhance neurogenesis and angiogenesis following brain injuries may provide promising opportunities to improve clinical outcomes and brain functional recovery. This review discusses neurogenesis and angiogenesis in the adult brain following stroke or TBI. Selected cell-based and pharmacological therapies are highlighted that promote neurogenesis and angiogenesis and are designed to restore neurological function after brain injuries. These discoveries emphasize the need for an improved understanding of injury- and therapy-induced neurogenesis and angiogenesis in the adult brain, and suggest that the manipulation of endogenous neural precursors and endothelial cells is a potential therapy for brain injury.
Figures
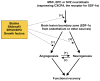
References
-
- Greve MW, Zink BJ. Pathophysiology of traumatic brain injury. Mt Sinai J Med. 2009;76(2):97–104. - PubMed
-
- Barone FC. Ischemic stroke intervention requires mixed cellular protection of the penumbra. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2009;10(3):220–223. - PubMed
-
- Narayan RK, Michel ME, Ansell B, Baethmann A, Biegon A, Bracken MB, Bullock MR, Choi SC, Clifton GL, Contant CF, Coplin WM, et al. Clinical trials in head injury. J Neurotrauma. 2002;19(5):503–557. An excellent early review of failed clinical trials in head injury from clinical, research, and pharmaceutical views. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
