Magnetic barcoded hydrogel microparticles for multiplexed detection
- PMID: 20178351
- PMCID: PMC2877154
- DOI: 10.1021/la904903g
Magnetic barcoded hydrogel microparticles for multiplexed detection
Abstract
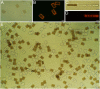
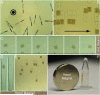
Magnetic polymer particles have been used in a wide variety of applications ranging from targeting and separation to diagnostics and imaging. Current synthesis methods have limited these particles to spherical or deformations of spherical morphologies. In this paper, we report the use of stop flow lithography to produce magnetic hydrogel microparticles with a graphical code region, a probe region, and a magnetic tail region. These anisotropic multifunctional magnetic polymer particles are an enhanced version of previously synthesized "barcoded" particles (Science, 2007, 315, 1393-1396) developed for the sensitive and rapid multiplexed sensing of nucleic acids. The newly added magnetic region has acquired dipole moments in the presence of weak homogeneous magnetic fields, allowing the particles to align along the applied field direction. The novel magnetic properties have led to practical applications in the efficient orientation and separation of the barcoded microparticles during biological assays without disrupting detection capabilities.
Figures
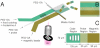

Similar articles
-
Post-synthesis functionalized hydrogel microparticles for high performance microRNA detection.Anal Chim Acta. 2019 Oct 17;1076:110-117. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2019.05.009. Epub 2019 May 7. Anal Chim Acta. 2019. PMID: 31203954
-
Colour-barcoded magnetic microparticles for multiplexed bioassays.Nat Mater. 2010 Sep;9(9):745-9. doi: 10.1038/nmat2815. Epub 2010 Aug 22. Nat Mater. 2010. PMID: 20729849
-
Encoded hydrogel microparticles with universal mismatch-incorporated DNA probes for highly specific multiplex detection of SNPs.Talanta. 2022 Aug 1;245:123480. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2022.123480. Epub 2022 Apr 15. Talanta. 2022. PMID: 35462139
-
Magnetic particles for the separation and purification of nucleic acids.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2006 Dec;73(3):495-504. doi: 10.1007/s00253-006-0675-0. Epub 2006 Oct 25. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2006. PMID: 17063328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Magnetism and microfluidics.Lab Chip. 2006 Jan;6(1):24-38. doi: 10.1039/b513005k. Epub 2005 Nov 28. Lab Chip. 2006. PMID: 16372066 Review.
Cited by
-
Photopolymerization-Based Synthesis of Uniform Magnetic Hydrogels and Colorimetric Glucose Detection.Materials (Basel). 2020 Oct 2;13(19):4401. doi: 10.3390/ma13194401. Materials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33023165 Free PMC article.
-
Release of magnetic nanoparticles from cell-encapsulating biodegradable nanobiomaterials.ACS Nano. 2012 Aug 28;6(8):6640-9. doi: 10.1021/nn300902w. Epub 2012 Jul 27. ACS Nano. 2012. PMID: 22680777 Free PMC article.
-
Highly Magnetized Encoded Hydrogel Microparticles with Enhanced Rinsing Capabilities for Efficient microRNA Detection.Biomedicines. 2021 Jul 20;9(7):848. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9070848. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34356912 Free PMC article.
-
Manipulating biological agents and cells in micro-scale volumes for applications in medicine.Chem Soc Rev. 2013 Jul 7;42(13):5788-808. doi: 10.1039/c3cs60042d. Chem Soc Rev. 2013. PMID: 23575660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integration of binding peptide selection and multifunctional particles as tool-box for capture of soluble proteins in serum.J R Soc Interface. 2014 Oct 6;11(99):20140718. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2014.0718. J R Soc Interface. 2014. PMID: 25100324 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Millman JR, Bhatt KH, Prevo BG, Velev OD. Nat. Mater. 2005;4:98–102. - PubMed
-
- Lee D, Cohen RE, Rubner MF. Langmuir. 2005;21:9651–9659. - PubMed
-
- Lee D, Cohen RE, Rubner MF. Langmuir. 2007;23:123–129. - PubMed
-
- Voltairas PA, Fotiadis DI, Michalis LK. J. Biomech. 2002;35:813–821. - PubMed
-
- Doyle PS, Bibette J, Bancaud A, Viovy JL. Science. 2002;295:2237–2237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

