Genetic diversity of NS5A protein from hepatitis C virus genotype 3a and its relationship to therapy response
- PMID: 20178583
- PMCID: PMC2838888
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-10-36
Genetic diversity of NS5A protein from hepatitis C virus genotype 3a and its relationship to therapy response
Abstract
Background: The quasispecies nature of HCV may have important implications for viral persistence, pathogenicity and resistance to antiviral agents. The variability of one of the viral proteins, NS5A, is believed to be related to the response to IFN therapy, the standard treatment for infection. In this study we analyzed the quasispecies composition of NS5A protein in patients infected with HCV genotype 3a, before IFN therapy.
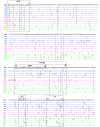
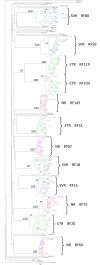
Methods: Viral RNA was isolated from samples of 12 patients: four sustained virological responders (SVR), four non-responders (NR), and four end-of-treatment responders (ETR). cDNA was synthesized, the NS5A region was amplified and the fragments obtained were cloned. Fifteen clones from each patient were sequenced with eight primers, generating 179 contigs.
Results: Higher values for substitution (either synonymous or non-synonymous) and for distance were found in the SVR group. However, the NR group showed relatively more non-synonymous mutations than the other groups, owing to the higher values of dN/dS in complete NS5A and most specific regions. Overall, NS5A protein is undergoing purifying selection, since all dN/dS ratios values are below 0.5.
Conclusions: Our study provides an overview of the genetic variability of complete NS5A protein in HCV genotype 3a.
Figures
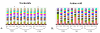
References
-
- Silva LK, Parana R, Souza SP, Berby F, Kay A, Trepo C, Santana N, Cotrim H, Lyra LG, Reis MG. Hepatitis C virus genotypes in a northeastern area of Brazil. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2000;62(2):257–260. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

