Cyclooxygenase-2 enhances alpha2beta1 integrin expression and cell migration via EP1 dependent signaling pathway in human chondrosarcoma cells
- PMID: 20178602
- PMCID: PMC2837621
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-43
Cyclooxygenase-2 enhances alpha2beta1 integrin expression and cell migration via EP1 dependent signaling pathway in human chondrosarcoma cells
Abstract
Background: Cyclooxygenase (COX)-2, the inducible isoform of prostaglandin (PG) synthase, has been implicated in tumor metastasis. Interaction of COX-2 with its specific EP receptors on the surface of cancer cells has been reported to induce cancer invasion. However, the effects of COX-2 on migration activity in human chondrosarcoma cells are mostly unknown. In this study, we examined whether COX-2 and EP interaction are involved in metastasis of human chondrosarcoma.
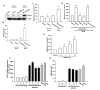
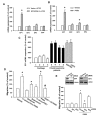
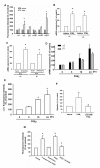
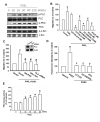
Results: We found that over-expression of COX-2 or exogenous PGE2 increased the migration of human chondrosarcoma cells. We also found that human chondrosarcoma tissues and chondrosarcoma cell lines had significant expression of the COX-2 which was higher than that in normal cartilage. By using pharmacological inhibitors or activators or genetic inhibition by the EP receptors, we discovered that the EP1 receptor but not other PGE receptors is involved in PGE2-mediated cell migration and alpha2beta1 integrin expression. Furthermore, we found that human chondrosarcoma tissues expressed a higher level of EP1 receptor than normal cartilage. PGE2-mediated migration and integrin up-regulation were attenuated by phospholipase C (PLC), protein kinase C (PKC) and c-Src inhibitor. Activation of the PLCbeta, PKCalpha, c-Src and NF-kappaB signaling pathway after PGE2 treatment was demonstrated, and PGE2-induced expression of integrin and migration activity were inhibited by the specific inhibitor, siRNA and mutants of PLC, PKC, c-Src and NF-kappaB cascades.
Conclusions: Our results indicated that PGE2 enhances the migration of chondrosarcoma cells by increasing alpha2beta1 integrin expression through the EP1/PLC/PKCalpha/c-Src/NF-kappaB signal transduction pathway.
Figures
References
-
- Yuan J, Dutton CM, Scully SP. RNAi mediated MMP-1 silencing inhibits human chondrosarcoma invasion. J Orthop Res. 2005;23:1467–1474. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

