Genetic and functional characterization of putative Ras/Raf interaction inhibitors in C. elegans and mammalian cells
- PMID: 20178605
- PMCID: PMC2848644
- DOI: 10.1186/1750-2187-5-2
Genetic and functional characterization of putative Ras/Raf interaction inhibitors in C. elegans and mammalian cells
Abstract
Background: Activation of the mammalian Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK MAPK signaling cascade promotes cellular proliferation, and activating Ras mutations are implicated in cancer onset and maintenance. This pathway, a therapeutic target of interest, is highly conserved and required for vulval development in C. elegans. Gain-of-function mutations in the Ras ortholog lead to constitutive pathway signaling and a multivulva (Muv) phenotype. MCP compounds were identified in a yeast two-hybrid screen for their ability to disrupt Ras-Raf interactions. However, this had not been confirmed in another system, and conflicting results were reported regarding selective MCP-mediated blockade of Ras- and Raf-mediated biological activities in mammalian cells. Here we used the easily-scored Muv phenotype as an in vivo readout to characterize the selectivity of MCP110 and its analogs, and performed biochemical studies in mammalian cells to determine whether MCP treatment results in impaired interaction between Ras and its effector Raf.
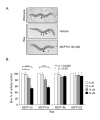
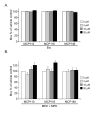
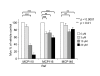
Results: Our genetic analyses showed significant dose-dependent MCP-mediated reduction of Muv in C. elegans strains with activating mutations in orthologs of Ras (LET-60) or Raf (LIN-45), but not MAP kinases or an Ets-like transcription factor. Thus, these inhibitors selectively impair pathway function downstream of Ras and upstream of or at the level of Raf, consistent with disruption of the Ras/Raf interaction. Our biochemical analyses of MCP110-mediated disruption of Ras-Raf interactions in mammalian cells showed that MCP110 dose-dependently reduced Raf-RBD pulldown of Ras, displaced a fluorescently-tagged Raf-RBD probe from plasma membrane locations of active Ras to the cytosol and other compartments, and decreased active, phosphorylated ERK1/2.
Conclusions: We have effectively utilized C. elegans as an in vivo genetic system to evaluate the activity and selectivity of inhibitors intended to target the Ras-Raf-MAPK pathway. We demonstrated the ability of MCP110 to disrupt, at the level of Ras/Raf, the Muv phenotype induced by chronic activation of this pathway in C. elegans. In mammalian cells, we not only demonstrated MCP-mediated blockade of the physical interaction between Ras and Raf, but also narrowed the site of interaction on Raf to the RBD, and showed consequent functional impairment of the Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK pathway in both in vivo and cell-based systems.
Figures


Similar articles
-
MEK-2, a Caenorhabditis elegans MAP kinase kinase, functions in Ras-mediated vulval induction and other developmental events.Genes Dev. 1995 Mar 15;9(6):742-55. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.6.742. Genes Dev. 1995. PMID: 7729690
-
A two-hybrid approach to identify inhibitors of the RAS-RAF interaction.Enzymes. 2013;33 Pt A:213-48. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-416749-0.00010-5. Epub 2013 Aug 8. Enzymes. 2013. PMID: 25033807 Review.
-
Inhibitors of Ras/Raf-1 interaction identified by two-hybrid screening revert Ras-dependent transformation phenotypes in human cancer cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Oct 29;99(22):14398-403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.222222699. Epub 2002 Oct 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12391290 Free PMC article.
-
Caenorhabditis elegans lin-45 raf is essential for larval viability, fertility and the induction of vulval cell fates.Genetics. 2002 Feb;160(2):481-92. doi: 10.1093/genetics/160.2.481. Genetics. 2002. PMID: 11861555 Free PMC article.
-
LET-23-mediated signal transduction during Caenorhabditis elegans development.Mol Reprod Dev. 1995 Dec;42(4):523-8. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1080420422. Mol Reprod Dev. 1995. PMID: 8607985 Review.
Cited by
-
Drugging the undruggable RAS: Mission possible?Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014 Nov;13(11):828-51. doi: 10.1038/nrd4389. Epub 2014 Oct 17. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014. PMID: 25323927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological targeting of RAS: Recent success with direct inhibitors.Pharmacol Res. 2019 Jan;139:503-511. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2018.10.021. Epub 2018 Oct 23. Pharmacol Res. 2019. PMID: 30366101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The complex journey of targeting RAS in oncology.BMC Cancer. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):1053. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14033-y. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40597785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Direct small-molecule inhibitors of KRAS: from structural insights to mechanism-based design.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2016 Nov;15(11):771-785. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2016.139. Epub 2016 Jul 29. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2016. PMID: 27469033 Review.
-
Small molecule inhibitors of RAS-effector protein interactions derived using an intracellular antibody fragment.Nat Commun. 2018 Aug 9;9(1):3169. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05707-2. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30093669 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bos JL. ras oncogenes in human cancer: a review. Cancer Res. 1989;49:4682–4689. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

