PhiC31 recombination system demonstrates heritable germinal transmission of site-specific excision from the Arabidopsis genome
- PMID: 20178628
- PMCID: PMC2837860
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6750-10-17
PhiC31 recombination system demonstrates heritable germinal transmission of site-specific excision from the Arabidopsis genome
Abstract
Background: The large serine recombinase phiC31 from broad host range Streptomyces temperate phage, catalyzes the site-specific recombination of two recognition sites that differ in sequence, typically known as attachment sites attB and attP. Previously, we characterized the phiC31 catalytic activity and modes of action in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe.
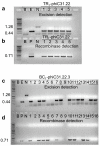
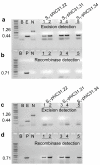
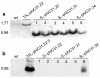
Results: In this work, the phiC31 recombinase gene was placed under the control of the Arabidopsis OXS3 promoter and introduced into Arabidopsis harboring a chromosomally integrated attB and attP-flanked target sequence. The phiC31 recombinase excised the attB and attP-flanked DNA, and the excision event was detected in subsequent generations in the absence of the phiC31 gene, indicating germinal transmission was possible. We further verified that the genomic excision was conservative and that introduction of a functional recombinase can be achieved through secondary transformation as well as manual crossing.
Conclusion: The phiC31 system performs site-specific recombination in germinal tissue, a prerequisite for generating stable lines with unwanted DNA removed. The precise site-specific deletion by phiC31 in planta demonstrates that the recombinase can be used to remove selectable markers or other introduced transgenes that are no longer desired and therefore can be a useful tool for genome engineering in plants.
Figures


Similar articles
-
ParA resolvase catalyzes site-specific excision of DNA from the Arabidopsis genome.Transgenic Res. 2009 Apr;18(2):237-48. doi: 10.1007/s11248-008-9213-4. Epub 2008 Aug 14. Transgenic Res. 2009. PMID: 18704739
-
The Bxb1 recombination system demonstrates heritable transmission of site-specific excision in Arabidopsis.BMC Biotechnol. 2012 Mar 21;12:9. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-12-9. BMC Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22436504 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo evaluation of PhiC31 recombinase activity using a self-excision cassette.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Nov;36(20):e134. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn627. Epub 2008 Oct 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18829714 Free PMC article.
-
Streptomyces temperate bacteriophage integration systems for stable genetic engineering of actinomycetes (and other organisms).J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012 May;39(5):661-72. doi: 10.1007/s10295-011-1069-6. Epub 2011 Dec 13. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22160317 Review.
-
[Progress of φC31 integrase system in site-specific integration].Yi Chuan. 2011 Jun;33(6):567-75. doi: 10.3724/sp.j.1005.2011.00567. Yi Chuan. 2011. PMID: 21684861 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Use of phage φC31 integrase as a tool for zebrafish genome manipulation.Methods Cell Biol. 2011;104:195-208. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-374814-0.00011-2. Methods Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21924164 Free PMC article.
-
Less is more: strategies to remove marker genes from transgenic plants.BMC Biotechnol. 2013 Apr 23;13:36. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-13-36. BMC Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23617583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
phiC31 integrase-mediated site-specific recombination in barley.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45353. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045353. Epub 2012 Sep 14. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23024817 Free PMC article.
-
Transgene excision in pollen using a codon optimized serine resolvase CinH-RS2 site-specific recombination system.Plant Mol Biol. 2011 Apr;75(6):621-31. doi: 10.1007/s11103-011-9756-2. Epub 2011 Feb 26. Plant Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21359553
-
Generation of a selectable marker free, highly expressed single copy locus as landing pad for transgene stacking in sugarcane.Plant Mol Biol. 2019 Jun;100(3):247-263. doi: 10.1007/s11103-019-00856-4. Epub 2019 Mar 27. Plant Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30919152
References
-
- Cellini F, Chesson A, Colquhoun I, Constable A, Davies HV, Engel KH, Gatehouse AM, Karenlampi S, Kok EJ, Leguay JJ, Lehesranta S, Noteborn HP, Pedersen J, Smith M. Unintended effects and their detection in genetically modified crops. Food Chem Toxicol. 2004;42:1089–1125. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2004.02.003. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

