Timing is everything: cell cycle control of Rad52
- PMID: 20178629
- PMCID: PMC2838861
- DOI: 10.1186/1747-1028-5-7
Timing is everything: cell cycle control of Rad52
Abstract
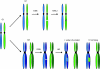
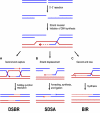
Regulation of the repair of DNA double-strand breaks by homologous recombination is extremely important for both cell viability and the maintenance of genomic integrity. Modulation of double-strand break repair in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae involves controlling the recruitment of one of the central recombination proteins, Rad52, to sites of DNA lesions. The Rad52 protein, which plays a role in strand exchange and the annealing of single strand DNA, is positively regulated upon entry into S phase, repressed during the intra-S phase checkpoint, and undergoes posttranslational modification events such as phosphorylation and sumoylation. These processes all contribute to the timing of Rad52 recruitment, its stability and function. Here, we summarize the regulatory events affecting the Rad52 protein and discuss how this regulation impacts DNA repair and cell survival.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Control of Rad52 recombination activity by double-strand break-induced SUMO modification.Nat Cell Biol. 2006 Nov;8(11):1284-90. doi: 10.1038/ncb1488. Epub 2006 Oct 1. Nat Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 17013376
-
Cell cycle-regulated centers of DNA double-strand break repair.Cell Cycle. 2003 Sep-Oct;2(5):479-83. Cell Cycle. 2003. PMID: 12963848
-
Rad52 Inverse Strand Exchange Drives RNA-Templated DNA Double-Strand Break Repair.Mol Cell. 2017 Jul 6;67(1):19-29.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.05.019. Epub 2017 Jun 8. Mol Cell. 2017. PMID: 28602639 Free PMC article.
-
Reappearance from Obscurity: Mammalian Rad52 in Homologous Recombination.Genes (Basel). 2016 Sep 14;7(9):63. doi: 10.3390/genes7090063. Genes (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27649245 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of rDNA stability by sumoylation.DNA Repair (Amst). 2009 Apr 5;8(4):507-16. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2009.01.015. Epub 2009 Mar 3. DNA Repair (Amst). 2009. PMID: 19261548 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeted gene addition to a predetermined site in the human genome using a ZFN-based nicking enzyme.Genome Res. 2012 Jul;22(7):1316-26. doi: 10.1101/gr.122879.111. Epub 2012 Mar 20. Genome Res. 2012. PMID: 22434427 Free PMC article.
-
Oral administration of M13-loaded nanoliposomes is safe and effective to treat colitis-associated cancer in mice.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2023 Jul-Dec;20(10):1443-1462. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2023.2231345. Epub 2023 Jul 2. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2023. PMID: 37379034 Free PMC article.
-
RDM1 gene overexpression represents a therapeutic target in papillary thyroid carcinoma.Endocr Connect. 2017 Nov;6(8):700-707. doi: 10.1530/EC-17-0209. Epub 2017 Sep 22. Endocr Connect. 2017. PMID: 28939762 Free PMC article.
-
Genome editing in Kluyveromyces and Ogataea yeasts using a broad-host-range Cas9/gRNA co-expression plasmid.FEMS Yeast Res. 2018 May 1;18(3):foy012. doi: 10.1093/femsyr/foy012. FEMS Yeast Res. 2018. PMID: 29438517 Free PMC article.
-
Invasive oral cancer stem cells display resistance to ionising radiation.Oncotarget. 2015 Dec 22;6(41):43964-77. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6268. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26540568 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguilera A, Rothstein R. Molecular Genetics of Recombination. Berlin-Heidelberg: Springer; 2007.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

