Regulation and dysregulation of immunoglobulin E: a molecular and clinical perspective
- PMID: 20178634
- PMCID: PMC2837605
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-7961-8-3
Regulation and dysregulation of immunoglobulin E: a molecular and clinical perspective
Abstract
Background: Altered levels of Immunoglobulin E (IgE) represent a dysregulation of IgE synthesis and may be seen in a variety of immunological disorders. The object of this review is to summarize the historical and molecular aspects of IgE synthesis and the disorders associated with dysregulation of IgE production.
Methods: Articles published in Medline/PubMed were searched with the keyword Immunoglobulin E and specific terms such as class switch recombination, deficiency and/or specific disease conditions (atopy, neoplasia, renal disease, myeloma, etc.). The selected papers included reviews, case reports, retrospective reviews and molecular mechanisms. Studies involving both sexes and all ages were included in the analysis.
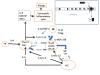
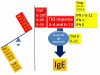
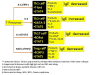
Results: Both very low and elevated levels of IgE may be seen in clinical practice. Major advancements have been made in our understanding of the molecular basis of IgE class switching including roles for T cells, cytokines and T regulatory (or Treg) cells in this process. Dysregulation of this process may result in either elevated IgE levels or IgE deficiency.
Conclusion: Evaluation of a patient with elevated IgE must involve a detailed differential diagnosis and consideration of various immunological and non-immunological disorders. The use of appropriate tests will allow the correct diagnosis to be made. This can often assist in the development of tailored treatments.
Figures



References
-
- Williams AF, Barclay AN. The immunoglobulin superfamily--domains for cell surface recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:381–405. - PubMed
-
- Chi DS, Fitzgerald SM, Krishnaswamy G. Mast cell histamine and cytokine assays. Methods Mol Biol. 2006;315:203–215. - PubMed
-
- Krishnaswamy G, Ajitawi O, Chi DS. The human mast cell: an overview. Methods Mol Biol. 2006;315:13–34. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

