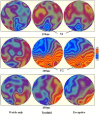
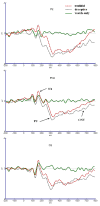
Event-related potential measures of the intending process: time course and related ERP components
- PMID: 20178644
- PMCID: PMC2848189
- DOI: 10.1186/1744-9081-6-15
Event-related potential measures of the intending process: time course and related ERP components
Abstract
Background: The intending process plays an important part to the successful completion of many daily activities. However, few researchers have paid attention to this issue. This study was set to investigate the time course and the electrophysiological evidence of the intending process with a cue-respond task.
Methods: Event-related potentials (ERPs) were recorded while participants were performing different cued conditions (deceptive, truthful, and watch-only). The time course of intending process was analyzed through the different effect of the cue stimuli.
Results: The P2 component, that appeared between 200 and 400 ms after the cue was onset, can be observed in the intended conditions (deceptive, truthful), but cannot be found in un-intended condition (watch-only). The mean amplitude in P2 between the truthful and deceptive conditions was consistent with previous studies. P2 was thought to be the reflection of the intention process.
Conclusions: The results suggested that the intention process happened 200 to 400 ms after the cue stimuli was onset, and the P2 in the posterior scalp during this period could be a specific component that related with the process of intention.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential effects of practice on the executive processes used for truthful and deceptive responses: an event-related brain potential study.Brain Res Cogn Brain Res. 2005 Aug;24(3):386-404. doi: 10.1016/j.cogbrainres.2005.02.011. Epub 2005 Apr 7. Brain Res Cogn Brain Res. 2005. PMID: 16099352 Clinical Trial.
-
Response compatibility and the relationship between event-related potentials and the timing of a motor response.J Neurophysiol. 1996 Dec;76(6):3705-13. doi: 10.1152/jn.1996.76.6.3705. J Neurophysiol. 1996. PMID: 8985868 Clinical Trial.
-
Isolating event-related potential components associated with voluntary control of visuo-spatial attention.Brain Res. 2008 Aug 28;1227:96-109. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.06.034. Epub 2008 Jun 20. Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18621037 Clinical Trial.
-
Event-related potentials as a measure of sleep disturbance: a tutorial review.Noise Health. 2010 Apr-Jun;12(47):137-53. doi: 10.4103/1463-1741.63216. Noise Health. 2010. PMID: 20472959 Review.
-
Event-related potential measures of the inhibition of information processing: II. The sleep onset period.Int J Psychophysiol. 2002 Dec;46(3):197-214. doi: 10.1016/s0167-8760(02)00112-5. Int J Psychophysiol. 2002. PMID: 12445948 Review.
Cited by
-
Weighted Brain Network Metrics for Decoding Action Intention Understanding Based on EEG.Front Hum Neurosci. 2020 Jul 2;14:232. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2020.00232. eCollection 2020. Front Hum Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32714168 Free PMC article.
-
The presentation order of cue and target matters in deception study.Behav Brain Funct. 2010 Oct 22;6:63. doi: 10.1186/1744-9081-6-63. Behav Brain Funct. 2010. PMID: 20964866 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Sweet Taste on Romantic Semantic Processing: An ERP Study.Front Psychol. 2019 Jul 9;10:1573. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01573. eCollection 2019. Front Psychol. 2019. PMID: 31354580 Free PMC article.
-
Facial and semantic emotional interference: a pilot study on the behavioral and cortical responses to the Dual Valence Association Task.Behav Brain Funct. 2011 Apr 13;7:8. doi: 10.1186/1744-9081-7-8. Behav Brain Funct. 2011. PMID: 21489277 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources