The prevalence of hypertension, obesity and dyslipidemia in individuals of over 30 years of age belonging to minorities from the pasture area of Xinjiang
- PMID: 20178648
- PMCID: PMC2838812
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-10-91
The prevalence of hypertension, obesity and dyslipidemia in individuals of over 30 years of age belonging to minorities from the pasture area of Xinjiang
Abstract
Background: The prevalence of population-wide hypertension, obesity and dyslipidemia has not been well studied in the pasture area of Xinjiang. The present epidemiological study was performed to determine the prevalence of hypertension, obesity and dyslipidemia in minority populations from the pasture area of Xinjiang and to discuss the potential risk factors for hypertension.
Methods: A population-based, cross-sectional study in the Xinjiang pasture area was performed which included 2251 participants aged over 30 years (90.33% participation rate) of whom 71.26% were Kazaks. Several risk factors were considered: hypertension (defined as systolic or diastolic blood pressure or both of at least 140/90 mmHg measured on one occasion or treatment for hypertension) overweight/obesity (body mass index > or = 25 kg/m2) alcohol intake, smoking/tobacco use and dyslipidemia. Outcomes were prevalence of hypertension, obesity and dyslipidemia and the associated risk factors of hypertension detected by multivariate logistic regression analysis taking into account various metabolic and lifestyle characteristics.
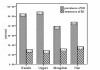
Results: The prevalence of hypertension, overweight/obesity and dyslipidemia in all participants from the pasture area of Xinjiang was 51.9%, 47.9% and 49.2% respectively. Independently, the prevalence and awareness of hypertension was 52.6% and 15.3% among Kazaks (n = 1604), 54.6% and 14.1% among Uygurs (n = 418), 39.5% and 16.1% among Mongolians (n = 81) and 43.9% and 18.2% among non-Xinjiang-born Han immigrants (n = 148). The prevalence of overweight/obesity in Kazaks, Uygurs, Mongolians and Han immigrants was 46.7%, 48.9%, 62.5% and 50.3%, respectively. The prevalence of dyslipidemia in the four ethnic groups mentioned was 53.5%, 34.8%, 49.3% and 47.3%, respectively. The mean blood pressure in all participants was 136/86 mmHg (pre-hypertensive), the mean BMI was 24.7 kg/m2. Based on multiple logistic regression analysis, the significant risk factors for hypertension were age [1.07(1.06-1.09), P < 0.0001], overweight/obesity [overweight: 1.61(1.22-2.13), p = 0.0007; obesity: 1.95 (1.33-2.87), p = 0.0007], hypercholesterolemia [1.30(1.15-1.47), p < 0.0001] and an alcohol intake of over 30 g/day [2.22(1.43-3.45), p = 0.0004].
Conclusions: The considerably high prevalence of hypertension, overweight/obesity and dyslipidemia among the minority population aged over 30 from the pasture area of Xinjiang calls for effective preventive measures. Age, increased body mass index, hypercholesterolemia and > or =30 g/d alcohol intake can be counted as risk factors for hypertension, but further genetic or environmental clarification would be desirable to explain the unusually high prevalence of the conditions mentioned above.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Analysis on epidemiological characteristics and related factors of dyslipidemia among adult residents of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region during 2013-2014].Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2018 Nov 6;52(11):1152-1157. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2018.11.011. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 30419700 Chinese.
-
Prevalence of dyslipidemia and associated risk factors among adults aged ≥35 years in northern China: a cross-sectional study.BMC Public Health. 2020 Jul 6;20(1):1068. doi: 10.1186/s12889-020-09172-9. BMC Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32631296 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced hypertension prevalence in non-Han Chinese minorities from Xinjiang Province, China.Hypertens Res. 2009 Dec;32(12):1097-103. doi: 10.1038/hr.2009.159. Epub 2009 Sep 25. Hypertens Res. 2009. PMID: 19779488 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and risk factors of hypertension among Hui population in China: A systematic review and meta-analysis based on 30,565 study participants.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 May 7;100(18):e25192. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000025192. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 33950917 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of metabolic syndrome and obesity-associated hypertension in the racial ethnic minorities of the United States.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2014 Jul;16(7):449. doi: 10.1007/s11906-014-0449-5. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2014. PMID: 24819559 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Body size and abnormal lipids among adult patients at the Baptist Medical centre, Ogbomoso, Nigeria.Afr Health Sci. 2013 Mar;13(1):32-7. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v13i1.5. Afr Health Sci. 2013. PMID: 23658565 Free PMC article.
-
Association between high cytomegalovirus antibody titers and blood pressure in the adult Kazakh and Han Chinese populations.Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2017 Oct;129(19-20):709-716. doi: 10.1007/s00508-017-1239-2. Epub 2017 Aug 3. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2017. PMID: 28776103
-
Relationship between urinary sodium with blood pressure and hypertension among a Kazakh community population in Xinjiang, China.J Hum Hypertens. 2017 May;31(5):333-340. doi: 10.1038/jhh.2016.83. Epub 2017 Jan 5. J Hum Hypertens. 2017. PMID: 28054572
-
Obesity and Heath-Carter Somatotyping of 3438 Adults in the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region of China by Multivariate Analysis.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021 Feb 15;14:659-670. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S287954. eCollection 2021. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021. PMID: 33623401 Free PMC article.
-
An Evaluation on the Effect of Health Education and of Low-Dose Statin in Dyslipidemia among Low-Income Rural Uyghur Adults in Far Western China: A Comprehensive Intervention Study.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2015 Sep 11;12(9):11410-21. doi: 10.3390/ijerph120911410. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2015. PMID: 26378561 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Ministry of Health of the People's Republic of China. http://www.moh.gov.cn/publicfiles/business/htmlfiles/mohwsbwstjxxzx/s820...
-
- Wolf MK, Cooper RS, Banegas JR, Giampaoli S, Hense HW, Joffres M, Kastarinen M, Poulter N, Primatesta P, Rodríguez-Artalejo F, Stegmayr B, Thamm M, Tuomilehto J, Vanuzzo D, Vescio F. Hypertension prevalence and blood pressure levels in 6 European countries, Canada, and the United States. JAMA. 2003;289:2363–2369. doi: 10.1001/jama.289.18.2363. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical