Elevated ATPase activity of KaiC applies a circadian checkpoint on cell division in Synechococcus elongatus
- PMID: 20178745
- PMCID: PMC3031423
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.12.042
Elevated ATPase activity of KaiC applies a circadian checkpoint on cell division in Synechococcus elongatus
Abstract
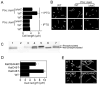
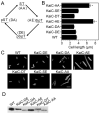
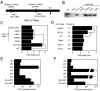
A circadian clock coordinates physiology and behavior in diverse groups of living organisms. Another major cyclic cellular event, the cell cycle, is regulated by the circadian clock in the few cases where linkage of these cycles has been studied. In the cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus, the circadian clock gates cell division by an unknown mechanism. Using timelapse microscopy, we confirm the gating of cell division in the wild-type and demonstrate the regulation of cytokinesis by key clock components. Specifically, a state of the oscillator protein KaiC that is associated with elevated ATPase activity closes the gate by acting through a known clock output pathway to inhibit FtsZ ring formation at the division site. An activity that stimulates KaiC phosphorylation independently of the KaiA protein was also uncovered. We propose a model that separates the functions of KaiC ATPase and phosphorylation in cell division gating and other circadian behaviors.
2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Comment in
-
Circadian cell-cycle progression: Cracking open the gate.Cell. 2010 Feb 19;140(4):458-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.02.002. Cell. 2010. PMID: 20178739
Similar articles
-
A novel allele of kaiA shortens the circadian period and strengthens interaction of oscillator components in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942.J Bacteriol. 2009 Jul;191(13):4392-400. doi: 10.1128/JB.00334-09. Epub 2009 Apr 24. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 19395479 Free PMC article.
-
Autonomous synchronization of the circadian KaiC phosphorylation rhythm.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2007 Nov;14(11):1084-8. doi: 10.1038/nsmb1312. Epub 2007 Oct 28. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17965725
-
Role of KaiC phosphorylation in the circadian clock system of Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Sep 21;101(38):13927-32. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0403906101. Epub 2004 Sep 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15347812 Free PMC article.
-
How a cyanobacterium tells time.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2008 Dec;11(6):541-6. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2008.10.003. Epub 2008 Nov 10. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18983934 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A cyanobacterial circadian clock based on the Kai oscillator.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2007;72:47-55. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2007.72.029. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2007. PMID: 18419262 Review.
Cited by
-
Rhythmic ring-ring stacking drives the circadian oscillator clockwise.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Oct 16;109(42):16847-51. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1211508109. Epub 2012 Sep 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22967510 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the circadian clock of cyanobacteria.Integr Comp Biol. 2013 Jul;53(1):93-102. doi: 10.1093/icb/ict054. Epub 2013 May 10. Integr Comp Biol. 2013. PMID: 23667047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tracking and visualizing the circadian ticking of the cyanobacterial clock protein KaiC in solution.EMBO J. 2011 Jan 5;30(1):68-78. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2010.298. Epub 2010 Nov 26. EMBO J. 2011. PMID: 21113137 Free PMC article.
-
Single mutations in sasA enable a simpler ΔcikA gene network architecture with equivalent circadian properties.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Nov 25;111(47):E5069-75. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1419902111. Epub 2014 Nov 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25385627 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of glycogen metabolism in circadian control of UV resistance in cyanobacteria.PLoS Genet. 2020 Nov 30;16(11):e1009230. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009230. eCollection 2020 Nov. PLoS Genet. 2020. PMID: 33253146 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chabot JR, Pedraza JM, Luitel P, van Oudenaarden A. Stochastic gene expression out-of-steady-state in the cyanobacterial circadian clock. Nature. 2007;450:1249–1252. - PubMed
-
- Chen Z, Odstrcil EA, Tu BP, McKnight SL. Restriction of DNA replication to the reductive phase of the metabolic cycle protects genome integrity. Science. 2007;316:1916–1919. - PubMed
-
- Clerico EM, Ditty JL, Golden SS. Methods in molecular biology. Vol. 362. Clifton, NJ: 2007. Specialized techniques for site-directed mutagenesis in cyanobacteria; pp. 155–171. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

