Mice lacking Mrp1 have reduced testicular steroid hormone levels and alterations in steroid biosynthetic enzymes
- PMID: 20178799
- PMCID: PMC2862834
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2010.02.019
Mice lacking Mrp1 have reduced testicular steroid hormone levels and alterations in steroid biosynthetic enzymes
Abstract
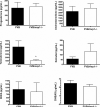
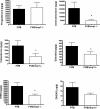
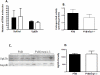
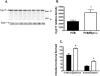
The multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 (MRP1/ABCC1) is a member of the ABC active transporter family that can transport several steroid hormone conjugates, including 17beta-estradiol glucuronide, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEAS), and estrone 3-sulfate. The present study investigated the role that MRP1 plays in maintaining proper hormone levels in the serum and testes. Serum and testicular steroid hormone levels were examined in both wild-type mice and Mrp1 null mice. Serum testosterone levels were reduced 5-fold in mice lacking Mrp1, while testicular androstenedione, testosterone, estradiol, and dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) were significantly reduced by 1.7- to 4.5-fold in Mrp1 knockout mice. Investigating the mechanisms responsible for the reduction in steroid hormones in Mrp1-/- mice revealed no differences in the expression or activity of enzymes that inactivate steroids, the sulfotransferases or glucuronosyltransferases. However, steroid biosynthetic enzyme levels in the testes were altered. Cyp17 protein levels were increased by 1.6-fold, while Cyp17 activity using progesterone as a substrate was also increased by 1.4- to 2.0-fold in mice lacking Mrp1. Additionally, the ratio of 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase to 3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, and steroidogenic factor 1 to 3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase were significantly increased in the testes of Mrp1-/- mice. These results indicate that Mrp1-/- mice have lowered steroid hormones levels, and suggests that upregulation of steroid biosynthetic enzymes may be an attempt to maintain proper steroid hormone homeostasis.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Anakwe OO, Payne AH. Noncoordinate regulation of de novo synthesis of cytochrome P450 cholesterol side-chain cleavage and cytochrome P45017α-hdryoxylase C17-20 lyase in mouse Leydig cell cultures: relation to steroid production. Mol. Endocrinol . 1987;1:595–603. - PubMed
-
- Andersen ME, Thomas RS, Gaido KW, Conolly RB. Dose-response modeling in reproductive toxicology in the systems biology era. Reprod.Toxicol. 2005;19:327–337. - PubMed
-
- Ankley GT, Bencic DC, Cavallin JE, Jensen KM, Kahl MD, Makynen EA, Martinovic D, Mueller ND, Wehmas LC, Villeneuve DL. Dynamic nature of alterations in the endocrine system of fathead minnows exposed to the fungicide prochloraz. Toxicol. Sci. 2009;112:344–353. - PubMed
-
- Aye IL, Paxton JW, Evseenko DA, Keelan JA. Expression, localisation and activity of ATP binding cassette (ABC) family of drug transporters in human amnion membranes. Placenta. 2007;28:868–877. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

