Fas apoptosis inhibitory molecule regulates T cell receptor-mediated apoptosis of thymocytes by modulating Akt activation and Nur77 expression
- PMID: 20178987
- PMCID: PMC2852919
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.072744
Fas apoptosis inhibitory molecule regulates T cell receptor-mediated apoptosis of thymocytes by modulating Akt activation and Nur77 expression
Abstract
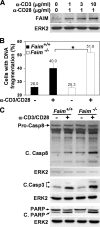
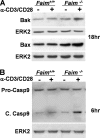
Fas apoptosis inhibitory molecule (FAIM) has been demonstrated to confer resistance to Fas-induced apoptosis of lymphocytes and hepatocytes in vitro and in vivo. Here, we show that FAIM is up-regulated in thymocytes upon T cell receptor (TCR) engagement and that faim(-/-) thymocytes are highly susceptible to TCR-mediated apoptosis with increased activation of caspase-8 and -9. Furthermore, injection of anti-CD3 antibodies leads to augmented depletion of CD4(+)CD8(+) T cells in the thymus of faim(-/-) mice compared with wild-type control, suggesting that FAIM plays a role in thymocyte apoptosis. Cross-linking of the TCR on faim(-/-) thymocytes leads to an elevated protein level of the orphan nuclear receptor Nur77, which plays a role in thymocyte apoptosis. Interestingly, in the absence of FAIM, there are reduced ubiquitination and degradation of the Nur77 protein. Faim(-/-) thymocytes also exhibit a defective TCR-induced activation of Akt whose activity we now show is required for Nur77 ubiquitination. Further analyses utilizing FAIM-deficient primary thymocytes and FAIM-overexpressing DO-11.10 T cells indicate that FAIM acts upstream of Akt during TCR signaling and influences the localization of Akt to lipid rafts, hence affecting its activation. Taken together, our study defined a TCR-induced FAIM/Akt/Nur77 signaling axis that is critical for modulating the apoptosis of developing thymocytes.
Figures



References
-
- Rathmell J. C., Thompson C. B. (2002) Cell 109, S97–107 - PubMed
-
- Sohn S. J., Rajpal A., Winoto A. (2003) Curr. Opin. Immunol. 15, 209–216 - PubMed
-
- Dhein J., Walczak H., Bäumler C., Debatin K. M., Krammer P. H. (1995) Nature 373, 438–441 - PubMed
-
- Moulian N., Berrih-Aknin S. (1998) Semin. Immunol. 10, 449–456 - PubMed
-
- Werlen G., Hausmann B., Naeher D., Palmer E. (2003) Science 299, 1859–1863 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

