Integrative analysis of the melanoma transcriptome
- PMID: 20179022
- PMCID: PMC2847744
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.103697.109
Integrative analysis of the melanoma transcriptome
Abstract
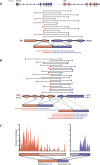
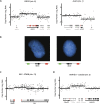
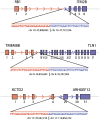
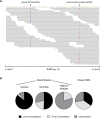
Global studies of transcript structure and abundance in cancer cells enable the systematic discovery of aberrations that contribute to carcinogenesis, including gene fusions, alternative splice isoforms, and somatic mutations. We developed a systematic approach to characterize the spectrum of cancer-associated mRNA alterations through integration of transcriptomic and structural genomic data, and we applied this approach to generate new insights into melanoma biology. Using paired-end massively parallel sequencing of cDNA (RNA-seq) together with analyses of high-resolution chromosomal copy number data, we identified 11 novel melanoma gene fusions produced by underlying genomic rearrangements, as well as 12 novel readthrough transcripts. We mapped these chimeric transcripts to base-pair resolution and traced them to their genomic origins using matched chromosomal copy number information. We also used these data to discover and validate base-pair mutations that accumulated in these melanomas, revealing a surprisingly high rate of somatic mutation and lending support to the notion that point mutations constitute the major driver of melanoma progression. Taken together, these results may indicate new avenues for target discovery in melanoma, while also providing a template for large-scale transcriptome studies across many tumor types.
Figures


References
-
- Albert TJ, Molla MN, Muzny DM, Nazareth L, Wheeler D, Song X, Richmond TA, Middle CM, Rodesch MJ, Packard CJ, et al. Direct selection of human genomic loci by microarray hybridization. Nat Methods. 2007;4:903–905. - PubMed
-
- Blacker D, Wilcox MA, Laird NM, Rodes L, Horvath SM, Go RC, Perry R, Watson B, Jr, Bassett SS, McInnis MG, et al. Alpha-2 macroglobulin is genetically associated with Alzheimer disease. Nat Genet. 1998;19:357–360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
