Nonsense-mediated RNA decay regulation by cellular stress: implications for tumorigenesis
- PMID: 20179151
- PMCID: PMC2841721
- DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-09-0502
Nonsense-mediated RNA decay regulation by cellular stress: implications for tumorigenesis
Abstract
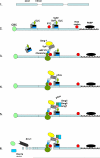
Nonsense-mediated RNA decay (NMD) has long been viewed as an important constitutive mechanism to rapidly eliminate mutated mRNAs. More recently, it has been appreciated that NMD also degrades multiple nonmutated transcripts and that NMD can be regulated by wide variety of cellular stresses. Many of the stresses that inhibit NMD, including cellular hypoxia and amino acid deprivation, are experienced in cells exposed to hostile microenvironments, and several NMD-targeted transcripts promote cellular adaptation in response to these environmental stresses. Because adaptation to the microenvironment is crucial in tumorigenesis, and because NMD targets many mutated tumor suppressor gene transcripts, the regulation of NMD may have particularly important implications in cancer. This review briefly outlines the mechanisms by which transcripts are identified and targeted by NMD and reviews the evidence showing that NMD is a regulated process that can dynamically alter gene expression. Although much of the focus in NMD research has been in identifying the proteins that play a role in NMD and identifying NMD-targeted transcripts, recent data about the potential functional significance of NMD regulation, including the stabilization of alternatively spliced mRNA isoforms, the validation of mRNAs as bona fide NMD targets, and the role of NMD in tumorigenesis, are explored.
Figures

References
-
- Frischmeyer PA, Dietz HC. Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in health and disease. Hum Mol Genet. 1999;8(10):1893–900. - PubMed
-
- Mendell JT, Sharifi NA, Meyers JL, Martinez-Murillo F, Dietz HC. Nonsense surveillance regulates expression of diverse classes of mammalian transcripts and mutes genomic noise. Nat Genet. 2004;36(10):1073–8. - PubMed
-
- Clement SL, Lykke-Andersen J. A tethering approach to study proteins that activate mRNA turnover in human cells. Methods Mol Biol. 2008;419:121–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

