Rac1 targeting suppresses p53 deficiency-mediated lymphomagenesis
- PMID: 20179179
- PMCID: PMC2858481
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2009-02-202440
Rac1 targeting suppresses p53 deficiency-mediated lymphomagenesis
Abstract
Mutation of the p53 tumor suppressor is associated with disease progression, therapeutic resistance, and poor prognosis in patients with lymphoid malignancies and can occur in approximately 50% of Burkitt lymphomas. Thus, new therapies are needed to specifically target p53-deficient lymphomas with increased efficacy. In the current study, the specific impact of inhibition of the small GTPase Rac1 on p53-deficient B- and T-lymphoma cells was investigated. p53 deficiency resulted in increased Rac1 activity in both B-cell and T-cell lines, and its suppression was able to abrogate p53 deficiency-mediated lymphoma cell proliferation. Further, Rac targeting resulted in increased apoptosis via a p53-independent mechanism. By probing multiple signaling axes and performing rescue studies, we show that the antiproliferative effect of Rac1 targeting in lymphoma cells may involve the PAK and Akt signaling pathway, but not the mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathway. The effects of inhibition of Rac1 were extended in vivo where Rac1 targeting was able to specifically impair p53-deficient lymphoma cell growth in mouse xenografts and postpone lymphomagenesis onset in murine transplantation models. Because the Rac1 signaling axis is a critical determinant of apoptosis and tumorigenesis, it may represent an important basis for therapy in the treatment of p53-deficient lymphomas.
Figures
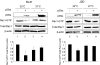
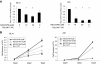

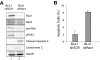
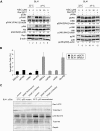


References
-
- Jaffe ES, Diebold J, Harris NL, Muller-Hermelink HK, Flandrin G, Vardiman JW. Burkitt's lymphoma: a single disease with multiple variants: the World Health Organization classification of neoplastic diseases of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. Blood. 1999;93:1124. - PubMed
-
- Harris NL, Horning SJ. Burkitt's lymphoma–the message from microarrays. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:2495–2498. - PubMed
-
- Adams JM. Oncogene activation by fusion of chromosomes in leukaemia. Nature. 1985;315:541–542. - PubMed
-
- Bhatia K, Gutierrez M, Magrath IT. Burkitt's lymphoma cells frequently carry monoallelic DJ rearrangements. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1992;182:319–324. - PubMed
-
- Capoulade C, Bressac-de Paillerets B, Lefrere I, et al. Overexpression of MDM2, due to enhanced translation, results in inactivation of wild-type p53 in Burkitt's lymphoma cells. Oncogene. 1998;16:1603–1610. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

