FGFR1 amplification drives endocrine therapy resistance and is a therapeutic target in breast cancer
- PMID: 20179196
- PMCID: PMC2832818
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3746
FGFR1 amplification drives endocrine therapy resistance and is a therapeutic target in breast cancer
Abstract
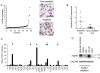
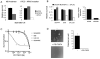
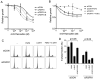
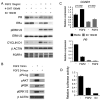
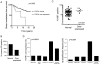
Amplification of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1) occurs in approximately 10% of breast cancers and is associated with poor prognosis. However, it is uncertain whether overexpression of FGFR1 is causally linked to the poor prognosis of amplified cancers. Here, we show that FGFR1 overexpression is robustly associated with FGFR1 amplification in two independent series of breast cancers. Breast cancer cell lines with FGFR1 overexpression and amplification show enhanced ligand-dependent signaling, with increased activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase and phosphoinositide 3-kinase-AKT signaling pathways in response to FGF2, but also show basal ligand-independent signaling, and are dependent on FGFR signaling for anchorage-independent growth. FGFR1-amplified cell lines show resistance to 4-hydroxytamoxifen, which is reversed by small interfering RNA silencing of FGFR1, suggesting that FGFR1 overexpression also promotes endocrine therapy resistance. FGFR1 signaling suppresses progesterone receptor (PR) expression in vitro, and likewise, amplified cancers are frequently PR negative, identifying a potential biomarker for FGFR1 activity. Furthermore, we show that amplified cancers have a high proliferative rate assessed by Ki67 staining and that FGFR1 amplification is found in 16% to 27% of luminal B-type breast cancers. Our data suggest that amplification and overexpression of FGFR1 may be a major contributor to poor prognosis in luminal-type breast cancers, driving anchorage-independent proliferation and endocrine therapy resistance.
Figures
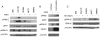
Comment in
-
Genetic alterations of FGF receptors: an emerging field in clinical cancer diagnostics and therapeutics.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2010 Sep;10(9):1375-9. doi: 10.1586/era.10.128. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2010. PMID: 20836672
References
-
- Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2000;406:747–52. - PubMed
-
- Loi S, Haibe-Kains B, Desmedt C, et al. Definition of clinically distinct molecular subtypes in estrogen receptor-positive breast carcinomas through genomic grade. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:1239–46. - PubMed
-
- Paik S, Shak S, Tang G, et al. A multigene assay to predict recurrence of tamoxifen-treated, node-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:2817–26. - PubMed
-
- Courjal F, Cuny M, Simony-Lafontaine J, et al. Mapping of DNA amplifications at 15 chromosomal localizations in 1875 breast tumors: definition of phenotypic groups. Cancer research. 1997;57:4360–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

