Chronic cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition promotes myofibroblast-associated intestinal fibrosis
- PMID: 20179298
- PMCID: PMC2833233
- DOI: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-09-0146
Chronic cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition promotes myofibroblast-associated intestinal fibrosis
Abstract
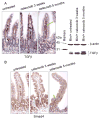
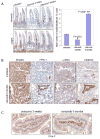
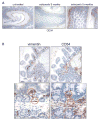
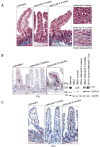
Anti-inflammatory drugs prevent intestinal tumor formation, an activity related to their ability to inhibit inflammatory pathway signaling in the target tissue. We previously showed that treatment of Min/(+) mice with the selective cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitor celecoxib induced rapid tumor regression; however, drug-resistant tumors appeared with long-term treatment. In this study, we investigated whole-tissue changes in inflammatory signaling by studying constituents of the tissue stroma and extracellular matrix. We found that celecoxib resistance was associated with changes in factors regulating autocrine transforming growth factor-beta (TGFbeta) signaling. Chronic drug treatment expanded the population of bone marrow-derived CD34(+) vimentin(+) alphaSMA(-) myofibroblast precursors and alphaSMA(+) vimentin(+) F4/80(-) myofibroblasts in the lamina propria and submucosa, providing a source of increased TGFbeta and COX-2 expression. Membrane constituents regulating TGFbeta availability, including syndecan-1 and heparanase-1, were also modified by chronic treatment in a manner promoting increased TGFbeta signaling. Finally, long-term celecoxib treatment induced tissue fibrosis, as indicated by increased expression of collagen, fibronectin, and laminin in the basement membrane. We conclude that chronic COX-2 inhibition alters TGFbeta signaling in the intestinal mucosa, producing conditions consistent with chronic inflammation.
Figures

References
-
- Waddell WR, Ganser GF, Cerise EJ, Loughry RW. Sulindac for polyposis of the colon. The American Journal of Surgery. 1989;157:175–9. - PubMed
-
- Steinbach G, Lynch PM, Phillips RKS, et al. The effect of celecoxib, a cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, in familial adenomatous polyposis. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2000;342(26):1946–52. - PubMed
-
- Arber N, Eagle CJ, Spicak J, et al. Celecoxib for the prevention of colorectal adenomatous polyps. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(9):885–95. - PubMed
-
- Bertagnolli MM. Chemoprevention of colorectal cancer with cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors: two steps forward, one step back. Lancet Oncology. 2007;8:439–43. - PubMed
-
- Solomon SD, McMurray JJ, Pfeffer MA, et al. Cardiovascular risk associated with celecoxib in a clinical trial for colorectal adenoma prevention. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(11):1071–80. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

