Relationships among reading skills of adults with low literacy
- PMID: 20179307
- PMCID: PMC3269070
- DOI: 10.1177/0022219409359343
Relationships among reading skills of adults with low literacy
Abstract
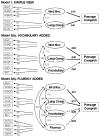
In this study, confirmatory factor analyses were used to examine the interrelationships among latent factors of the simple view model of reading comprehension (word recognition and language comprehension) and hypothesized additional factors (vocabulary and reading fluency) in a sample of 476 adult learners with low literacy levels. The results provided evidence for reliable distinctions between word recognition, fluency, language comprehension, and vocabulary skills as components of reading. Even so, the data did not support the hypothesis that the simple view needs to be expanded to include vocabulary or fluency factors, as has been posited in a few prior studies of younger and more able readers. Rather, word recognition and language comprehension alone were found to account adequately for variation in reading comprehension in adults with low literacy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bringing the Simple View of Reading to the clinic: Relationships between oral and written language skills in a clinical sample.J Commun Disord. 2016 Jul-Aug;62:147-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jcomdis.2016.07.002. Epub 2016 Jul 5. J Commun Disord. 2016. PMID: 27428381
-
Speaking up for vocabulary: reading skill differences in young adults.J Learn Disabil. 2007 May-Jun;40(3):226-43. doi: 10.1177/00222194070400030401. J Learn Disabil. 2007. PMID: 17518215 Free PMC article.
-
Native Korean-Speaking Children Learning to Read in English: A Structural Analysis of L2-English Literacy Acquisition.J Psycholinguist Res. 2019 Apr;48(2):391-415. doi: 10.1007/s10936-018-9610-7. J Psycholinguist Res. 2019. PMID: 30370498
-
Phonics training for English-speaking poor readers.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Nov 14;11(11):CD009115. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009115.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30480759 Free PMC article.
-
On the importance of listening comprehension.Int J Speech Lang Pathol. 2014 Jun;16(3):199-207. doi: 10.3109/17549507.2014.904441. Int J Speech Lang Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24833426 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Involvement of the right hemisphere in reading comprehension: a DTI study.Brain Res. 2014 Sep 25;1582:34-44. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.05.034. Epub 2014 Jun 5. Brain Res. 2014. PMID: 24909792 Free PMC article.
-
Early Elementary Grade Dual Language Learners from Spanish-speaking Homes Struggling with English Reading Comprehension: The Dormant Role of Language Skills.J Educ Psychol. 2020 Jul;112(5):880-894. doi: 10.1037/edu0000402. Epub 2019 Aug 1. J Educ Psychol. 2020. PMID: 33311734 Free PMC article.
-
Examining Sources and Mechanisms of Reading Comprehension Difficulties: Comparing English Learners and Non-English Learners within the Simple View of Reading.J Educ Psychol. 2019 Aug;111(6):982-1000. doi: 10.1037/edu0000332. Epub 2019 Jan 17. J Educ Psychol. 2019. PMID: 31435078 Free PMC article.
-
Vocabulary does not complicate the simple view of reading.Read Writ. 2016;29:435-451. doi: 10.1007/s11145-015-9608-6. Epub 2015 Dec 17. Read Writ. 2016. PMID: 26941478 Free PMC article.
-
It's in the Way That You Use It: How Vocabulary Knowledge and Usage Predict Writing Quality Among Adult Basic Education Learners.J Psycholinguist Res. 2022 Oct;51(5):1023-1041. doi: 10.1007/s10936-022-09877-5. Epub 2022 May 7. J Psycholinguist Res. 2022. PMID: 35524832 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adlof SM, Catts HW, Little TD. Should the simple view of reading include a fluency component? Reading and Writing. 2006;19(9):933–958.
-
- Anderson RC, Freebody P. Vocabulary knowledge. In: Guthrie JT, editor. Comprehension and teaching. Newark, DE: International Reading Association; 1981. pp. 77–117.
-
- Assink EM, Sandra D, editors. Reading complex words: Cross-language studies. New York: Springer; 2003.
-
- Bagozzi RP, Yi Y. On the evaluation of structural equation models. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science. 1992;16:74–94.
-
- Beck IL, McKeown MG. Conditions of vocabulary acquisition. In: Barr R, Karmil ML, Mosenthal PB, Pearson DD, editors. Handbook of reading research. II. New York: Longman Publishing Group; 1991. pp. 749–814.
- Bentler PM. EQS for Windows 6.1. [Computer software] Encino, CA: Multivariate Software, Inc; 1985–2006.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

