Accommodation of structural rearrangements in the huntingtin-interacting protein 1 coiled-coil domain
- PMID: 20179344
- PMCID: PMC2827350
- DOI: 10.1107/S0907444909054535
Accommodation of structural rearrangements in the huntingtin-interacting protein 1 coiled-coil domain
Abstract
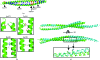
Huntingtin-interacting protein 1 (HIP1) is an important link between the actin cytoskeleton and clathrin-mediated endocytosis machinery. HIP1 has also been implicated in the pathogenesis of Huntington's disease. The binding of HIP1 to actin is regulated through an interaction with clathrin light chain. Clathrin light chain binds to a flexible coiled-coil domain in HIP1 and induces a compact state that is refractory to actin binding. To understand the mechanism of this conformational regulation, a high-resolution crystal structure of a stable fragment from the HIP1 coiled-coil domain was determined. The flexibility of the HIP1 coiled-coil region was evident from its variation from a previously determined structure of a similar region. A hydrogen-bond network and changes in coiled-coil monomer interaction suggest that the HIP1 coiled-coil domain is uniquely suited to allow conformational flexibility.
Figures
References
-
- Akey, D. L., Malashkevich, V. N. & Kim, P. S. (2001). Biochemistry, 40, 6352–6360. - PubMed
-
- Burkhard, P., Kammerer, R. A., Steinmetz, M. O., Bourenkov, G. P. & Aebi, U. (2000). Structure, 8, 223–230. - PubMed
-
- Chen, C. Y. & Brodsky, F. M. (2005). J. Biol. Chem.280, 6109–6117. - PubMed
-
- Conway, J. F. & Parry, D. A. (1990). Int. J. Biol. Macromol.12, 328–334. - PubMed
-
- Drubin, D. G., Kaksonen, M., Toret, C. & Sun, Y. (2005). Novartis Found. Symp.269, 35–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

