Integrin alpha9beta1: Unique signaling pathways reveal diverse biological roles
- PMID: 20179422
- PMCID: PMC2900612
- DOI: 10.4161/cam.4.2.10900
Integrin alpha9beta1: Unique signaling pathways reveal diverse biological roles
Abstract
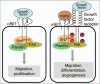
Integrins are transmembrane heterodimeric receptors responsible for transducing and modulating signals between the extracellular matrix and cytoskeleton, ultimately influencing cell functions such as adhesion and migration. Integrin alpha9beta1 is classified within a two member sub-family of integrins highlighted in part by its specialized role in cell migration. The importance of this role is demonstrated by its regulation of numerous biological functions including lymphatic valve morphogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, angiogenesis and hematopoietic homeostasis. Compared to other integrins the signaling mechanisms that transduce alpha9beta1-induced cell migration are not well described. We have recently shown that Src tyrosine kinase plays a key proximal role to control alpha9beta1 signaling. Specifically it activates inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and in turn nitric oxide (NO) production as a means to transduce cell migration. Furthermore, we have also described a role for FAK, Erk and Rac1 in alpha9beta1 signal transduction. Here we provide an over view of known integrin alpha9beta1 signaling pathways and highlight its roles in diverse biological conditions.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
