Carboetomidate: a pyrrole analog of etomidate designed not to suppress adrenocortical function
- PMID: 20179500
- PMCID: PMC2830733
- DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181cf40ed
Carboetomidate: a pyrrole analog of etomidate designed not to suppress adrenocortical function
Abstract
Background: Etomidate is a sedative hypnotic that is often used in critically ill patients because it provides superior hemodynamic stability. However, it also binds with high affinity to 11beta-hydroxylase, potently suppressing the synthesis of steroids by the adrenal gland that are necessary for survival. The authors report the results of studies to define the pharmacology of (R)-ethyl 1-(1-phenylethyl)-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylate (carboetomidate), a pyrrole analog of etomidate specifically designed not to bind with high affinity to 11beta-hydroxylase.
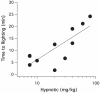
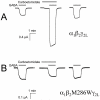
Methods: The hypnotic potency of carboetomidate was defined in tadpoles and rats using loss of righting reflex assays. Its ability to enhance wild-type alpha1beta2gamma2l and etomidate-insensitive mutant alpha1beta2M286Wgamma2l human gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor activities was assessed using electrophysiologic techniques. Its potency for inhibiting in vitro cortisol synthesis was defined using a human adrenocortical cell assay. Its effects on in vivo hemodynamic and adrenocortical function were defined in rats.
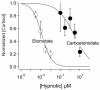
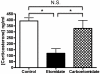
Results: Carboetomidate was a potent hypnotic in tadpoles and rats. It increased currents mediated by wild-type but not etomidate-insensitive mutant gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptors. Carboetomidate was a three orders of magnitude less-potent inhibitor of in vitro cortisol synthesis by adrenocortical cells than was etomidate. In rats, carboetomidate caused minimal hemodynamic changes and did not suppress adrenocortical function at hypnotic doses.
Conclusions: Carboetomidate is an etomidate analog that retains many beneficial properties of etomidate, but it is dramatically less potent as an inhibitor of adrenocortical steroid synthesis. Carboetomidate is a promising new sedative hypnotic for potential use in critically ill patients in whom adrenocortical suppression is undesirable.
Figures
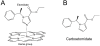
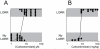
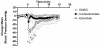
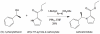
Similar articles
-
In vivo and in vitro pharmacological studies of methoxycarbonyl-carboetomidate.Anesth Analg. 2012 Aug;115(2):297-304. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3182320559. Epub 2011 Sep 29. Anesth Analg. 2012. PMID: 21965364 Free PMC article.
-
Methoxycarbonyl-etomidate: a novel rapidly metabolized and ultra-short-acting etomidate analogue that does not produce prolonged adrenocortical suppression.Anesthesiology. 2009 Aug;111(2):240-9. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181ae63d1. Anesthesiology. 2009. PMID: 19625798 Free PMC article.
-
Closed-loop continuous infusions of etomidate and etomidate analogs in rats: a comparative study of dosing and the impact on adrenocortical function.Anesthesiology. 2011 Oct;115(4):764-73. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e31821950de. Anesthesiology. 2011. PMID: 21572317 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of GABA Receptors in Anesthesia and Sedation: An Updated Review.CNS Drugs. 2025 Jan;39(1):39-54. doi: 10.1007/s40263-024-01128-6. Epub 2024 Oct 27. CNS Drugs. 2025. PMID: 39465449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical and molecular pharmacology of etomidate.Anesthesiology. 2011 Mar;114(3):695-707. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181ff72b5. Anesthesiology. 2011. PMID: 21263301 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The neurosteroid 5β-pregnan-3α-ol-20-one enhances actions of etomidate as a positive allosteric modulator of α1β2γ2L GABAA receptors.Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Dec;171(23):5446-57. doi: 10.1111/bph.12861. Br J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25117207 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of the EL-0052 as a potential anesthetic drug.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021 Jan 8;19:710-718. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.01.002. eCollection 2021. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 33510871 Free PMC article.
-
Binding site location on GABAA receptors determines whether mixtures of intravenous general anaesthetics interact synergistically or additively in vivo.Br J Pharmacol. 2019 Dec;176(24):4760-4772. doi: 10.1111/bph.14843. Epub 2019 Dec 11. Br J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31454409 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of GABA Receptor Agonists in Anesthesia and Sedation.CNS Drugs. 2017 Oct;31(10):845-856. doi: 10.1007/s40263-017-0463-7. CNS Drugs. 2017. PMID: 29039138 Review.
-
Sedative-hypnotic Binding to 11β-hydroxylase.Anesthesiology. 2016 Nov;125(5):943-951. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000001304. Anesthesiology. 2016. PMID: 27541316 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gooding JM, Weng JT, Smith RA, Berninger GT, Kirby RR. Cardiovascular and pulmonary responses following etomidate induction of anesthesia in patients with demonstrated cardiac disease. Anesth Analg. 1979;58:40–1. - PubMed
-
- Criado A, Maseda J, Navarro E, Escarpa A, Avello F. Induction of anaesthesia with etomidate: Haemodynamic study of 36 patients. Br J Anaesth. 1980;52:803–6. - PubMed
-
- Ebert TJ, Muzi M, Berens R, Goff D, Kampine JP. Sympathetic responses to induction of anesthesia in humans with propofol or etomidate. Anesthesiology. 1992;76:725–33. - PubMed
-
- Sarkar M, Laussen PC, Zurakowski D, Shukla A, Kussman B, Odegard KC. Hemodynamic responses to etomidate on induction of anesthesia in pediatric patients. Anesth Analg. 2005;101:645–50. - PubMed
-
- Fragen RJ, Shanks CA, Molteni A, Avram MJ. Effects of etomidate on hormonal responses to surgical stress. Anesthesiology. 1984;61:652–6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

