Processing of tumor antigen differentially impacts the development of helper and effector CD4+ T-cell responses
- PMID: 20179673
- PMCID: PMC2889742
- DOI: 10.1038/mt.2010.30
Processing of tumor antigen differentially impacts the development of helper and effector CD4+ T-cell responses
Abstract
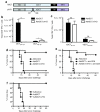
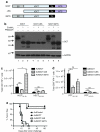
CD4(+) T cells contribute to the antitumor T-cell response as both effectors that promote tumor rejection and helpers that facilitate the activation of other antitumor effector cells, such as CD8(+) T cells. Maximal engagement of both effector and helper CD4(+) T-cell responses is a desirable attribute of cancer vaccines. We have employed the B16F10 murine melanoma model and a series of recombinant adenovirus (Ad) vaccines expressing mutant forms of the tumor antigen, dopachrome tautomerase, to investigate the relationship between antigen processing and the antitumor CD4(+) T-cell response. Our results have revealed an unexpected dichotomy in the generation of helper and effector CD4(+) T-cell responses where CD4(+) T effector responses are dependent upon protein processing and trafficking, whereas CD4(+) T helper responses are not. The results have important implications for strategies aimed at augmenting antigen immunogenicity by altering intracellular processing and localization.
Figures

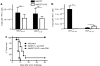
Similar articles
-
Tumor antigen-specific CD4+ T cells in cancer immunity: from antigen identification to tumor prognosis and development of therapeutic strategies.Tissue Antigens. 2014 Apr;83(4):237-46. doi: 10.1111/tan.12329. Tissue Antigens. 2014. PMID: 24641502 Review.
-
HCA587 Protein Vaccine Induces Specific Antitumor Immunity Mediated by CD4+ T-cells Expressing Granzyme B in a Mouse Model of Melanoma.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2021;21(6):738-746. doi: 10.2174/1871520620666200728131951. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 32723258
-
Specific T helper cell requirement for optimal induction of cytotoxic T lymphocytes against major histocompatibility complex class II negative tumors.J Exp Med. 1998 Mar 2;187(5):693-702. doi: 10.1084/jem.187.5.693. J Exp Med. 1998. PMID: 9480979 Free PMC article.
-
Immune responses to a class II helper peptide epitope in patients with stage III/IV resected melanoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2004 Aug 1;10(15):5004-13. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-0241. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15297401 Clinical Trial.
-
MHC class II-restricted tumor antigens recognized by CD4+ T cells: new strategies for cancer vaccine design.J Immunother. 2001 May-Jun;24(3):195-204. J Immunother. 2001. PMID: 11394496 Review.
Cited by
-
Oncolytic virus and PD-1/PD-L1 blockade combination therapy.Oncolytic Virother. 2018 Jul 31;7:65-77. doi: 10.2147/OV.S145532. eCollection 2018. Oncolytic Virother. 2018. PMID: 30105219 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combined vaccination and immunostimulatory antibodies provides durable cure of murine melanoma and induces transcriptional changes associated with positive outcome in human melanoma patients.Oncoimmunology. 2012 Jul 1;1(4):419-431. doi: 10.4161/onci.19534. Oncoimmunology. 2012. PMID: 22754760 Free PMC article.
-
Immunotherapy-induced CD8+ T cells instigate immune suppression in the tumor.Mol Ther. 2014 Jan;22(1):206-18. doi: 10.1038/mt.2013.255. Epub 2013 Oct 23. Mol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24196579 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang JC., and , Livingstone AM. Cutting edge: CD4+ T cell help can be essential for primary CD8+ T cell responses in vivo. J Immunol. 2003;171:6339–6343. - PubMed
-
- Gao FG, Khammanivong V, Liu WJ, Leggatt GR, Frazer IH., and , Fernando GJ. Antigen-specific CD4+ T-cell help is required to activate a memory CD8+ T cell to a fully functional tumor killer cell. Cancer Res. 2002;62:6438–6441. - PubMed
-
- Janssen EM, Lemmens EE, Wolfe T, Christen U, von Herrath MG., and , Schoenberger SP. CD4+ T cells are required for secondary expansion and memory in CD8+ T lymphocytes. Nature. 2003;421:852–856. - PubMed
-
- Shedlock DJ., and , Shen H. Requirement for CD4 T cell help in generating functional CD8 T cell memory. Science. 2003;300:337–339. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

