RAF inhibitors transactivate RAF dimers and ERK signalling in cells with wild-type BRAF
- PMID: 20179705
- PMCID: PMC3178447
- DOI: 10.1038/nature08902
RAF inhibitors transactivate RAF dimers and ERK signalling in cells with wild-type BRAF
Abstract
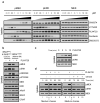
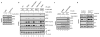
Tumours with mutant BRAF are dependent on the RAF-MEK-ERK signalling pathway for their growth. We found that ATP-competitive RAF inhibitors inhibit ERK signalling in cells with mutant BRAF, but unexpectedly enhance signalling in cells with wild-type BRAF. Here we demonstrate the mechanistic basis for these findings. We used chemical genetic methods to show that drug-mediated transactivation of RAF dimers is responsible for paradoxical activation of the enzyme by inhibitors. Induction of ERK signalling requires direct binding of the drug to the ATP-binding site of one kinase of the dimer and is dependent on RAS activity. Drug binding to one member of RAF homodimers (CRAF-CRAF) or heterodimers (CRAF-BRAF) inhibits one protomer, but results in transactivation of the drug-free protomer. In BRAF(V600E) tumours, RAS is not activated, thus transactivation is minimal and ERK signalling is inhibited in cells exposed to RAF inhibitors. These results indicate that RAF inhibitors will be effective in tumours in which BRAF is mutated. Furthermore, because RAF inhibitors do not inhibit ERK signalling in other cells, the model predicts that they would have a higher therapeutic index and greater antitumour activity than mitogen-activated protein kinase (MEK) inhibitors, but could also cause toxicity due to MEK/ERK activation. These predictions have been borne out in a recent clinical trial of the RAF inhibitor PLX4032 (refs 4, 5). The model indicates that promotion of RAF dimerization by elevation of wild-type RAF expression or RAS activity could lead to drug resistance in mutant BRAF tumours. In agreement with this prediction, RAF inhibitors do not inhibit ERK signalling in cells that coexpress BRAF(V600E) and mutant RAS.
Figures


Comment in
-
Drug discovery: inhibitors that activate.Nature. 2010 Mar 18;464(7287):358-9. doi: 10.1038/464358a. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20237552 No abstract available.
References
-
- Wellbrock C, et al. V599EB-RAF is an oncogene in melanocytes. Cancer Res. 2004;64:2338–42. - PubMed
-
- Chapman P, et al. Early efficacy signal demonstrated in advanced melanoma in a phase I trial of the oncogenic BRAF-selective inhibitor PLX4032 Eur. J. Cancer Suppl. 2009;7:5.
-
- Flaherty K, et al. Phase I study of PLX4032: Proof of concept for V600E BRAF mutation as a therapeutic target in human cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009;27 Abstract 9000.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

