Human urinary kallidinogenase suppresses cerebral inflammation in experimental stroke and downregulates nuclear factor-kappaB
- PMID: 20179726
- PMCID: PMC2949229
- DOI: 10.1038/jcbfm.2010.19
Human urinary kallidinogenase suppresses cerebral inflammation in experimental stroke and downregulates nuclear factor-kappaB
Abstract
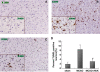
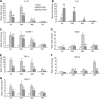
The purpose of this study is to investigate the possible mechanism and the neuroprotective effect of human urinary kallidinogenase (HUK) in cerebral ischemia. The mouse middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) model was used. Mice were treated with HUK (20 PNAU/g per day, intravenous) or saline as control, from the beginning of reperfusion to 72 h. Neurological deficits, infarct size, and BWC were measured at 6, 24, 48, and 72 h after MCAO, respectively. Pathological changes of brain were observed by TUNEL assay. Inflammatory factors were measured by real-time PCR and western blotting. Activation of MAPKs, Akt, and nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) was detected by western blotting. Our results indicated that HUK significantly improved neurofunction, decreased infarct size, and suppressed edema, as well as inflammatory mediators as compared with the vehicle group. Furthermore, HUK inhibited the NF-kappaB pathway and activated the MAPK/ERK pathway in this neuroprotection.
Figures


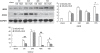
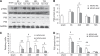
Similar articles
-
Human Urinary Kallidinogenase Promotes Angiogenesis and Cerebral Perfusion in Experimental Stroke.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 29;10(7):e0134543. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134543. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26222055 Free PMC article.
-
Ruscogenin reduces cerebral ischemic injury via NF-κB-mediated inflammatory pathway in the mouse model of experimental stroke.Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Aug 15;714(1-3):303-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.07.036. Epub 2013 Jul 30. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23911884
-
Time dependent neuroprotection of dexamethasone in experimental focal cerebral ischemia: The involvement of NF-κB pathways.Brain Res. 2018 Dec 15;1701:237-245. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2018.09.029. Epub 2018 Sep 21. Brain Res. 2018. PMID: 30248332
-
Intra-arterial human urinary kallidinogenase alleviates brain injury in rats with permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion through PI3K/AKT/FoxO1 signaling pathway.Brain Res. 2018 May 15;1687:129-136. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2018.02.049. Epub 2018 Mar 3. Brain Res. 2018. PMID: 29510144
-
Human urinary kallidinogenase combined with edaravone in treating acute ischemic stroke patients: A meta-analysis.Brain Behav. 2021 Dec;11(12):e2431. doi: 10.1002/brb3.2431. Epub 2021 Nov 22. Brain Behav. 2021. PMID: 34808033 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tissue Kallikrein Alleviates Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Activating the B2R-ERK1/2-CREB-Bcl-2 Signaling Pathway in Diabetic Rats.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:1843201. doi: 10.1155/2016/1843201. Epub 2016 Jun 30. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016. PMID: 27446506 Free PMC article.
-
Human Urinary Kallidinogenase decreases recurrence risk and promotes good recovery.Brain Behav. 2018 Aug;8(8):e01033. doi: 10.1002/brb3.1033. Epub 2018 Jul 20. Brain Behav. 2018. PMID: 30030910 Free PMC article.
-
Human Urinary Kallidinogenase Promotes Angiogenesis and Cerebral Perfusion in Experimental Stroke.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 29;10(7):e0134543. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134543. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26222055 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic investigation of transcription factors critical in the protection against cerebral ischemia by Danhong injection.Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 19;6:29823. doi: 10.1038/srep29823. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27431009 Free PMC article.
-
FasL-PDPK1 Pathway Promotes the Cytotoxicity of CD8+ T Cells During Ischemic Stroke.Transl Stroke Res. 2020 Aug;11(4):747-761. doi: 10.1007/s12975-019-00749-0. Epub 2020 Feb 8. Transl Stroke Res. 2020. PMID: 32036560
References
-
- Ali C, Nicole O, Docagne F, Lesne S, MacKenzie ET, Nouvelot A, Buisson A, Vivien D. Ischemia-induced interleukin-6 as a potential endogenous neuroprotective cytokine against NMDA receptor-mediated excitotoxicity in the brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2000;20:956–966. - PubMed
-
- Allan SM, Rothwell NJ. Cytokines and acute neurodegeneration. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001;2:734–744. - PubMed
-
- Barone FC, Feuerstein GZ. Inflammatory mediators and stroke: new opportunities for novel therapeutics. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1999;19:819–834. - PubMed
-
- Benveniste EN, Tang LP, Law RM. Differential regulation of astrocyte TNF-alpha expression by the cytokines TGF-beta, IL-6 and IL-10. Int J Dev Neurosci. 1995;13:341–349. - PubMed
-
- Bowen KK, Naylor M, Vemuganti R. Prevention of inflammation is a mechanism of preconditioning-induced neuroprotection against focal cerebral ischemia. Neurochem Int. 2006;49:127–135. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

