FcgammaRIIb inhibits allergic lung inflammation in a murine model of allergic asthma
- PMID: 20179765
- PMCID: PMC2825267
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009337
FcgammaRIIb inhibits allergic lung inflammation in a murine model of allergic asthma
Abstract
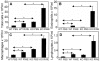
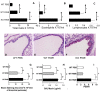
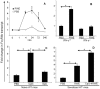
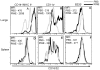
Allergic asthma is characterized by airway eosinophilia, increased mucin production and allergen-specific IgE. Fc gamma receptor IIb (FcgammaRIIb), an inhibitory IgG receptor, has recently emerged as a negative regulator of allergic diseases like anaphylaxis and allergic rhinitis. However, no studies to date have evaluated its role in allergic asthma. Our main objective was to study the role of FcgammaRIIb in allergic lung inflammation. We used a murine model of allergic airway inflammation. Inflammation was quantified by BAL inflammatory cells and airway mucin production. FcgammaRIIb expression was measured by qPCR and flow cytometry and the cytokines were quantified by ELISA. Compared to wild type animals, FcgammaRIIb deficient mice mount a vigorous allergic lung inflammation characterized by increased bronchoalveolar lavage fluid cellularity, eosinophilia and mucin content upon ragweed extract (RWE) challenge. RWE challenge in sensitized mice upregulated FcgammaRIIb in the lungs. Disruption of IFN-gamma gene abrogated this upregulation. Treatment of naïve mice with the Th1-inducing agent CpG DNA increased FcgammaRIIb expression in the lungs. Furthermore, treatment of sensitized mice with CpG DNA prior to RWE challenge induced greater upregulation of FcgammaRIIb than RWE challenge alone. These observations indicated that RWE challenge upregulated FcgammaRIIb in the lungs by IFN-gamma- and Th1-dependent mechanisms. RWE challenge upregulated FcgammaRIIb on pulmonary CD14+/MHC II+ mononuclear cells and CD11c+ cells. FcgammaRIIb deficient mice also exhibited an exaggerated RWE-specific IgE response upon sensitization when compared to wild type mice. We propose that FcgammaRIIb physiologically regulates allergic airway inflammation by two mechanisms: 1) allergen challenge mediates upregulation of FcgammaRIIb on pulmonary CD14+/MHC II+ mononuclear cells and CD11c+ cells by an IFN-gamma dependent mechanism; and 2) by attenuating the allergen specific IgE response during sensitization. Thus, stimulating FcgammaRIIb may be a therapeutic strategy in allergic airway disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
The inhibitory effects of intravenous administration of rabbit immunoglobulin G on airway inflammation are dependent upon Fcγ receptor IIb on CD11c(+) dendritic cells in a murine model.Clin Exp Immunol. 2010 Nov;162(2):315-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2010.04243.x. Epub 2010 Sep 1. Clin Exp Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20819092 Free PMC article.
-
Antigen-Specific IgG ameliorates allergic airway inflammation via Fcγ receptor IIB on dendritic cells.Respir Res. 2011 Apr 10;12(1):42. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-12-42. Respir Res. 2011. PMID: 21477339 Free PMC article.
-
Allergen challenge induces Ifng dependent GTPases in the lungs as part of a Th1 transcriptome response in a murine model of allergic asthma.PLoS One. 2009 Dec 21;4(12):e8172. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008172. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 20027288 Free PMC article.
-
IFN-gamma-inducing factor (IL-18) increases allergic sensitization, serum IgE, Th2 cytokines, and airway eosinophilia in a mouse model of allergic asthma.J Immunol. 2000 Mar 1;164(5):2701-10. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.5.2701. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10679111
-
Janus kinase-3 dependent inflammatory responses in allergic asthma.Int Immunopharmacol. 2010 Aug;10(8):829-36. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2010.04.014. Epub 2010 Apr 27. Int Immunopharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20430118 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The transcriptomic signature of respiratory sensitizers using an alveolar model.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024 Apr 8;40(1):21. doi: 10.1007/s10565-024-09860-x. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38584208 Free PMC article.
-
The contribution of allergen-specific IgG to the development of th2-mediated airway inflammation.J Allergy (Cairo). 2012;2012:236075. doi: 10.1155/2012/236075. Epub 2012 Oct 21. J Allergy (Cairo). 2012. PMID: 23150737 Free PMC article.
-
The inhibitory effects of intravenous administration of rabbit immunoglobulin G on airway inflammation are dependent upon Fcγ receptor IIb on CD11c(+) dendritic cells in a murine model.Clin Exp Immunol. 2010 Nov;162(2):315-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2010.04243.x. Epub 2010 Sep 1. Clin Exp Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20819092 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Fcgamma receptor polymorphisms are associated with human allergy.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 21;9(2):e89196. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089196. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24586589 Free PMC article.
-
SingleNucleotide Polymorphisms as Biomarkers of Mepolizumab and Benralizumab Treatment Response in Severe Eosinophilic Asthma.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 26;25(15):8139. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158139. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125709 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Laffargue M, Calvez R, Finan P, Trifilieff A, Barbier M, et al. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase gamma is an essential amplifier of mast cell function. Immunity. 2002;16:441–451. - PubMed
-
- Kawakami Y, Kitaura J, Satterthwaite AB, Kato RM, Asai K, et al. Redundant and opposing functions of two tyrosine kinases, Btk and Lyn, in mast cell activation. J Immunol. 2000;165:1210–1219. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

