Nanofluidic concentration devices for biomolecules utilizing ion concentration polarization: theory, fabrication, and applications
- PMID: 20179814
- PMCID: PMC2929016
- DOI: 10.1039/b822556g
Nanofluidic concentration devices for biomolecules utilizing ion concentration polarization: theory, fabrication, and applications
Abstract
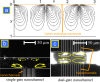
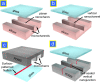
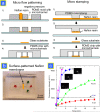
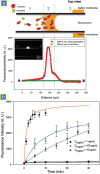
Recently, a new type of electrokinetic concentration devices has been developed in a microfluidic chip format, which allows efficient trapping and concentration of biomolecules by utilizing ion concentration polarization near nanofluidic structures. These devices have drawn much attention not only due to their potential application in biomolecule sensing, but also due to the rich scientific content related to ion concentration polarization, the underlying physical phenomenon for the operation of these electrokinetic concentration devices. This tutorial review provides an introduction to the scientific and engineering advances achieved, in-depth discussion about several interesting applications of these unique concentration devices, and their current limitations and challenges.
Figures






References
-
- Singh AK, Throckmorton DJ, Kirby BJ, Thompson AP. Micro Total Analysis Systems. Vol. 1. Kluwer Academic; Nara, Japan: 2002. pp. 347–349.
-
- Foote RS, Khandurina J, Jacobson SC, Ramsey JM. Anal. Chem. 2005;77:57–63. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y-C, Stevens AL, Han J. Anal. Chem. 2005;77:4293–4299. - PubMed
-
- Lichtenberg J, Verpoorte E, Rooij N. F. d. Electrophoresis. 2001;22:258–271. - PubMed
-
- Cui H, Horiuchi K, Dutta P, Ivory CF. Anal. Chem. 2005;77:7878–7886. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

