Ryanodine receptor channelopathies
- PMID: 20179962
- PMCID: PMC2885589
- DOI: 10.1007/s00424-010-0794-4
Ryanodine receptor channelopathies
Abstract
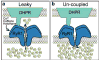
Ryanodine receptors (RyR) are intracellular Ca2+-permeable channels that provide the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release required for skeletal and cardiac muscle contractions. RyR1 underlies skeletal muscle contraction, and RyR2 fulfills this role in cardiac muscle. Over the past 20 years, numerous mutations in both RyR isoforms have been identified and linked to skeletal and cardiac diseases. Malignant hyperthermia, central core disease, and catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia have been genetically linked to mutations in either RyR1 or RyR2. Thus, RyR channelopathies are both of interest because they cause significant human diseases and provide model systems that can be studied to elucidate important structure-function relationships of these ion channels.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

