Molecular characterization of agonists that bind to an insect GABA receptor
- PMID: 20180551
- PMCID: PMC2852148
- DOI: 10.1021/bi901698c
Molecular characterization of agonists that bind to an insect GABA receptor
Abstract
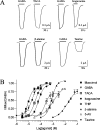
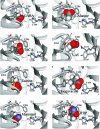
Ionotropic GABA receptors are widely distributed throughout the vertebrate and invertebrate central nervous system (CNS) where they mediate inhibitory neurotransmission. One of the most widely studied insect GABA receptors is constructed from RDL (resistance to dieldrin) subunits from Drosophila melanogaster. The aim of this study was to determine critical features of agonists binding to RDL receptors using in silico and experimental data. Partial atomic charges and dipole separation distances of a range of GABA analogues were calculated, and the potency of the analogues was determined using RDL receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. These data revealed functional agonists require an ammonium group and an acidic group with an optimum separation distance of approximately 5 A. To determine how the agonists bind to the receptor, a homology model of the extracellular domain was generated and agonists were docked into the binding site. The docking studies support the requirements for functional agonists and also revealed a range of potential interactions with binding site residues, including hydrogen bonds and cation-pi interactions. We conclude that the model and docking procedures yield a good model of the insect GABA receptor binding site and the location of agonists within it.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Actions of agonists, fipronil and ivermectin on the predominant in vivo splice and edit variant (RDLbd, I/V) of the Drosophila GABA receptor expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes.PLoS One. 2014 May 13;9(5):e97468. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097468. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24823815 Free PMC article.
-
GABA binding to an insect GABA receptor: a molecular dynamics and mutagenesis study.Biophys J. 2012 Nov 21;103(10):2071-81. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2012.10.016. Epub 2012 Nov 20. Biophys J. 2012. PMID: 23200041 Free PMC article.
-
Wild-type and insecticide-resistant homo-oligomeric GABA receptors of Drosophila melanogaster stably expressed in a Drosophila cell line.Neuropharmacology. 1996;35(9-10):1393-401. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(96)00087-1. Neuropharmacology. 1996. PMID: 9014156
-
Insect GABA receptors: splicing, editing, and targeting by antiparasitics and insecticides.Mol Pharmacol. 2005 Oct;68(4):942-51. doi: 10.1124/mol.105.015313. Epub 2005 Jul 18. Mol Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 16027231 Review.
-
Molecular biology of insect neuronal GABA receptors.Trends Neurosci. 1997 Dec;20(12):578-83. doi: 10.1016/s0166-2236(97)01127-2. Trends Neurosci. 1997. PMID: 9416671 Review.
Cited by
-
Contributions of γ-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) Receptors for the Activities of Pectis brevipedunculata Essential Oil against Drosophila suzukii and Pollinator Bees.Plants (Basel). 2024 May 17;13(10):1392. doi: 10.3390/plants13101392. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38794461 Free PMC article.
-
Stop the crop: Insights into the insecticidal mode of action of cinnamodial against mosquitoes.Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2021 Jan;171:104743. doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2020.104743. Epub 2020 Nov 8. Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33357565 Free PMC article.
-
The pharmacological profile of ELIC, a prokaryotic GABA-gated receptor.Neuropharmacology. 2012 Sep;63(4):761-7. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.05.027. Epub 2012 Jun 4. Neuropharmacology. 2012. PMID: 22677470 Free PMC article.
-
An atypical residue in the pore of Varroa destructor GABA-activated RDL receptors affects picrotoxin block and thymol modulation.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2014 Dec;55:19-25. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2014.10.002. Epub 2014 Oct 18. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 25460510 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome Analysis of the Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems of the Spider Cupiennius salei Reveals Multiple Putative Cys-Loop Ligand Gated Ion Channel Subunits and an Acetylcholine Binding Protein.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 14;10(9):e0138068. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138068. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26368804 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Harvey R. J.; Schmitt B.; Hermans-Borgmeyer I.; Gundelfinger E. D.; Betz H.; Darlison M. G. (1994) Sequence of a Drosophila ligand-gated ion-channel polypeptide with an unusual amino-terminal extracellular domain. J. Neurochem. 62, 2480–2483. - PubMed
-
- Henderson J. E.; Soderlund D. M.; Knipple D. C. (1993) Characterization of a putative γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor β subunit gene from Drosophila melanogaster. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 193, 474–482. - PubMed
-
- Sixma T. K.; Smit A. B. (2003) Acetylcholine binding protein (AChBP): A secreted glial protein that provides a high-resolution model for the extracellular domain of pentameric ligand-gated ion channels. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 32, 311–334. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

