Anthropometric comparison of mentally retarded males with and without the fragile X syndrome
- PMID: 2018070
- PMCID: PMC5463450
- DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.1320380220
Anthropometric comparison of mentally retarded males with and without the fragile X syndrome
Abstract
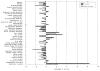
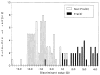
An anthropometric survey of 41 variables (weight, height, 10 linear, 4 breadth, 22 craniofacial, 2 skinfold, and testicular volume), including multivariate discriminant analysis, was undertaken on 110 mentally retarded males (39 with and 71 without the fra(X) syndrome). The mean Z scores of the fra(X) syndrome males fell between -2.00 and 8.38 for bizygomatic diameter and testicular volume, respectively, and the range of the mean Z scores of the non-fra(X) males was from -2.64 to 2.26 for hand breadth and testicular volume, respectively. There was a statistically significant difference (P less than .05) between fra(X) and non-fra(X) males for 18 measurements (weight, height, 7 linear, 2 breadth, 5 craniofacial, 1 skinfold, and testicular volume), with the greater measurements (excluding bizygomatic diameter) found in fra(X) males. Sitting height, knee-buttock length, middle finger length, and hand length were negatively correlated (P less than .05) with age, whereas bizygomatic diameter, ear length, and ear width were positively correlated (P less than .05) with age and head circumference, head length, and outer canthal distance were positively correlated (P less than .05) with fra(X) chromosome expression in the fra(X) males. Triceps and subscapular skinfold thicknesses were negatively correlated (P less than .05) with age, whereas ankle breadth, ear length, ear width, and nose length were positively correlated (P less than .05) in the non-fra(X) males. Discriminant analysis of 34 fra(X) and 71 non-fra(X) males resulted in a discriminant function based on 6 of 17 anthropometric variables and age.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Figures

References
-
- Blomquist HK, Bohman M, Edvinsson SO, Gillberg C, Gustavson K-H, Holmgren G, Wahlström J. Frequency of the fragile X syndrome in infantile autism: A Swedish multicenter study. Clin Genet. 1985;27:113–117. - PubMed
-
- Enslein K, Ralston A, Wilf HSC. Statistical Methods for Digital Computers. New York: John Wiley and Sons; 1977.
-
- Farkas LG. Anthropometry of the Head and Face in Medicine. New York: Elsevier Publishing Company; 1981.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
