Uncemented and cemented primary total hip arthroplasty in the Swedish Hip Arthroplasty Register
- PMID: 20180715
- PMCID: PMC2856202
- DOI: 10.3109/17453671003685400
Uncemented and cemented primary total hip arthroplasty in the Swedish Hip Arthroplasty Register
Abstract
Background and purpose: Since the introduction of total hip arthroplasty (THA) in Sweden, both components have most commonly been cemented. A decade ago the frequency of uncemented fixation started to increase, and this change in practice has continued. We therefore analyzed implant survival of cemented and uncemented THA, and whether the modes of failure differ between the two methods of fixation.
Patients and methods: All patients registered in the Swedish Hip Arthroplasty Register between 1992 and 2007 who received either totally cemented or totally uncemented THA were identified (n = 170,413). Kaplan-Meier survival analysis with revision of any component, and for any reason, as the endpoints was performed. Cox regression models were used to calculate risk ratios (RRs) for revision for various reasons, adjusted for sex, age, and primary diagnosis.
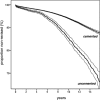
Results: Revision-free 10-year survival of uncemented THA was lower than that of cemented THA (85% vs. 94%, p < 0.001). No age or diagnosis groups benefited from the use of uncemented fixation. Cox regression analysis confirmed that uncemented THA had a higher risk of revision for any reason (RR = 1.5, 95% CI: 1.4-1.6) and for aseptic loosening (RR = 1.5, CI: 1.3-1.6). Uncemented cup components had a higher risk of cup revision due to aseptic loosening (RR = 1.8, CI: 1.6-2.0), whereas uncemented stem components had a lower risk of stem revision due to aseptic loosening (RR = 0.4, CI: 0.3-0.5) when compared to cemented components. Uncemented stems were more frequently revised due to periprosthetic fracture during the first 2 postoperative years than cemented stems (RR = 8, CI: 5-14). The 5 most common uncemented cups had no increased risk of revision for any reason when compared with the 5 most commonly used cemented cups (RR = 0.9, CI: 0.6-1.1). There was no significant difference in the risk of revision due to infection between cemented and uncemented THA.
Interpretation: Survival of uncemented THA is inferior to that of cemented THA, and this appears to be mainly related to poorer performance of uncemented cups. Uncemented stems perform better than cemented stems; however, unrecognized intraoperative femoral fractures may be an important reason for early failure of uncemented stems. The risk of revision of the most common uncemented cup designs is similar to that of cemented cups, indicating that some of the problems with uncemented cup fixation may have been solved.
Figures
References
-
- Badhe NP, Quinnell RC, Howard PW. The uncemented Bi-Contact total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2002;17:896–901. - PubMed
-
- Blacha J. High osteolysis and revision rate with the hydroxyapatite-coated ABG hip prostheses: 65 hips in 56 young patients followed for 5-9 years. Acta Orthop Scand. 2004;75:276–82. - PubMed
-
- Engesaeter LB, Lie SA, Espehaug B, Furnes O, Vollset SE, Havelin LI. Antibiotic prophylaxis in total hip arthroplasty: effects of antibiotic prophylaxis systemically and in bone cement on the revision rate of 22,170 primary hip replacements followed 0-14 years in the Norwegian Arthroplasty Register. Acta Orthop Scand. 2003;74:644–51. - PubMed
-
- Eskelinen A, Remes V, Helenius I, Pulkkinen P, Nevalainen J, Paavolainen P. Uncemented total hip arthroplasty for primary osteoarthritis in young patients: a mid-to long-term follow-up study from the Finnish Arthroplasty Register. Acta Orthop. 2006;77:57–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
