Glutathione S-transferase A4 is a positive marker for rat hepatic foci induced by clofibrate and genotoxic carcinogens
- PMID: 20180811
- PMCID: PMC11158787
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01508.x
Glutathione S-transferase A4 is a positive marker for rat hepatic foci induced by clofibrate and genotoxic carcinogens
Abstract
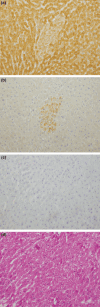
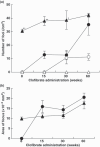
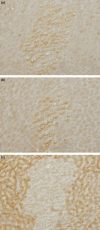
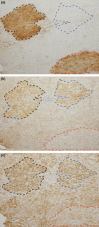
Peroxisome proliferators (PP), including clofibrate (CF), are non-genotoxic rodent carcinogens, and oxidative DNA damages are suggested as a causative event for carcinogenesis. Gene expression profiles differ between hepatic lesions induced by PP and genotoxic carcinogens. Our previous study revealed that expression of L-bifunctional enzyme (enoyl-CoA hydratase/3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase, BE) was repressed in preneoplastic lesions induced by PP, whereas it was enhanced in the surrounding tissues. In the present study, we immunohistochemically examined expression of the specific glutathione S-transferase (GST) form, GST-A4, which detoxifies 4-hydroxy-alkenal, the end-product of lipid peroxides, and nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), a transcription factor for many genes encoding drug-metabolizing enzymes and defending enzymes against oxidative stress, during rat hepatocarcinogenesis induced by CF and genotoxic carcinogens. GST-A4 and Nrf2 were not expressed in BE-negative foci at 8 weeks of CF administration, but were expressed in the foci at 60 weeks. GST-A4-positive foci appeared at later stages than BE-negative foci, but its localization was coincidental with that of the latter foci. The areas of GST-A4-positive foci were larger than those of BE-negative foci without GST-A4 expression. Most GST-A4-positive foci were also positive for Nrf2. In rat livers induced by genotoxic carcinogens, GST-P-negative foci as well as GST-P-positive foci were demonstrated. GST-A4 and Nrf2 were expressed in GST-P-negative foci, whereas they were not expressed in most GST-P-positive foci. Thus, GST-A4-positive foci developed in rat livers by CF and genotoxic carcinogen administration, indicating that the enzyme is a positive marker for hepatic foci induced by these different carcinogens.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lack of peroxisomal enzyme inducibility in rat hepatic preneoplastic lesions induced by mutagenic carcinogens: contrasted expression of glutathione S-transferase P form and enoyl CoA hydratase.Carcinogenesis. 1993 Mar;14(3):393-8. doi: 10.1093/carcin/14.3.393. Carcinogenesis. 1993. PMID: 8453714
-
Decreased expression of glutathione S-transferases and increased fatty change in peroxisomal enzyme-negative foci induced by clofibrate in rat livers.Carcinogenesis. 1995 Aug;16(8):1699-704. doi: 10.1093/carcin/16.8.1699. Carcinogenesis. 1995. PMID: 7634392
-
Different susceptibility to peroxisome proliferator-induced hepatocarcinogenesis in rats with polymorphic glutathione transferase genes.Cancer Sci. 2006 Aug;97(8):703-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2006.00247.x. Epub 2006 Jun 23. Cancer Sci. 2006. PMID: 16800819 Free PMC article.
-
Specific expression of glutathione S-transferase Pi forms in (pre)neoplastic tissues: their properties and functions.Tohoku J Exp Med. 1992 Oct;168(2):97-103. doi: 10.1620/tjem.168.97. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1992. PMID: 1306337 Review.
-
Value of GST-P positive preneoplastic hepatic foci in dose-response studies of hepatocarcinogenesis: evidence for practical thresholds with both genotoxic and nongenotoxic carcinogens. A review of recent work.Toxicol Pathol. 2003 Jan-Feb;31(1):80-6. doi: 10.1080/01926230390173879. Toxicol Pathol. 2003. PMID: 12597451 Review.
Cited by
-
Decrease of hepatic stellate cells in rats with enhanced sensitivity to clofibrate-induced hepatocarcinogenesis.Cancer Sci. 2011 Apr;102(4):735-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2011.01856.x. Epub 2011 Feb 10. Cancer Sci. 2011. PMID: 21214675 Free PMC article.
-
Glutathione S-transferase alpha 4 induction by activator protein 1 in colorectal cancer.Oncogene. 2016 Nov 3;35(44):5795-5806. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.113. Epub 2016 Apr 11. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 27065323 Free PMC article.
-
Discrimination of CpG Methylation Status and Nucleotide Differences in Tissue Specimen DNA by Oligoribonucleotide Interference-PCR.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 20;21(14):5119. doi: 10.3390/ijms21145119. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32698480 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Corton JC, Lapinskas PJ, Gonzales FJ. Central role of PPARalpha in the mechanism of action of hepatocarcinogenic peroxisome proliferators. Mutat Res 2000; 448: 139–51. - PubMed
-
- Svoboda DJ, Azarnoff DL. Tumors in male rats fed ethyl chlorophenoxyisobutyrate, a hypolipidemic drug. Cancer Res 1979; 39: 3419–28. - PubMed
-
- Reddy JK, Azarnoff DL, Hignite CE. Hypolipidemic hepatic peroxisome proliferators form a novel class of chemical carcinogenesis. Nature 1980; 283: 397–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

