Thrombin upregulates the angiopoietin-Tie2 Axis: endothelial protein C receptor occupancy prevents the thrombin mobilization of angiopoietin 2 and P-selectin from Weibel-Palade bodies
- PMID: 20180904
- PMCID: PMC2891946
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2010.03812.x
Thrombin upregulates the angiopoietin-Tie2 Axis: endothelial protein C receptor occupancy prevents the thrombin mobilization of angiopoietin 2 and P-selectin from Weibel-Palade bodies
Abstract
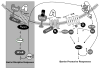
Summary background: Activated protein C (APC) in complex with endothelial protein C receptor (EPCR) can reverse the barrier-disruptive and cytotoxic effects of proinflammatory cytokines by cleaving protease-activated receptor 1 (PAR-1). Recently, it was reported that the PAR-1-dependent vascular barrier-protective effect of APC is mediated through transactivation of the angiopoietin (Ang)-Tie2 signaling pathway. The antagonist of this pathway, Ang2, is stored in Weibel-Palade bodies within endothelial cells.
Objectives: To determine whether the occupancy of EPCR by its ligand can switch the PAR-1-dependent signaling specificity of thrombin through the Ang-Tie2 axis.
Methods: We activated endothelial cells with thrombin before and after treating them with the catalytically inactive Ser195-->Ala substitution mutant of protein C. The expression levels of Ang1, Ang2 and Tie2 in response to thrombin were measured by both an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and a cell permeability assay in the absence and presence of small interfering RNA and a blocking antibody to Tie2.
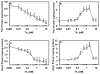
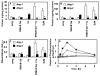
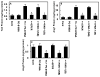
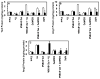
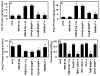
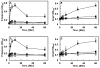
Results: Thrombin upregulated the expression of both Ang1 and Tie2 but downregulated the expression of Ang2 when EPCR was occupied by its ligand. The Ang1-Tie2-dependent protective effect of thrombin was initiated through protein C inhibiting the rapid mobilization of Ang2 from Weibel-Palade bodies. Interestingly, the protein C mutant also inhibited the thrombin mobilization of P-selectin.
Conclusions: These results suggest a physiologic role for the low concentration of thrombin in maintaining the integrity of the EPCR-containing vasculature through the PAR-1-dependent inhibition of Ang2 and P-selectin release from Weibel-Palade bodies.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Angiopoietin-mediated endothelial P-selectin translocation: cell signaling mechanisms.J Leukoc Biol. 2008 Feb;83(2):352-60. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0107056. Epub 2007 Nov 5. J Leukoc Biol. 2008. PMID: 17984290
-
Angiotensin AT(1) and AT(2) receptors differentially regulate angiopoietin-2 and vascular endothelial growth factor expression and angiogenesis by modulating heparin binding-epidermal growth factor (EGF)-mediated EGF receptor transactivation.Circ Res. 2001 Jan 19;88(1):22-9. doi: 10.1161/01.res.88.1.22. Circ Res. 2001. Retraction in: Circ Res. 2013 Jun 7;112(12):e180. doi: 10.1161/RES.0b013e31829b5cca. PMID: 11139469 Retracted.
-
The Tie-2 ligand angiopoietin-2 is stored in and rapidly released upon stimulation from endothelial cell Weibel-Palade bodies.Blood. 2004 Jun 1;103(11):4150-6. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-10-3685. Epub 2004 Feb 19. Blood. 2004. PMID: 14976056
-
The complex role of angiopoietin-2 in the angiopoietin-tie signaling pathway.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2012 Sep 1;2(9):a006550. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a006650. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2012. PMID: 22951441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiopoietin-2: development of inhibitors for cancer therapy.Curr Oncol Rep. 2009 Mar;11(2):111-6. doi: 10.1007/s11912-009-0017-3. Curr Oncol Rep. 2009. PMID: 19216842 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Titanium is a potent inducer of contact activation: implications for intravascular devices.J Thromb Haemost. 2023 May;21(5):1200-1213. doi: 10.1016/j.jtha.2022.12.014. Epub 2022 Dec 22. J Thromb Haemost. 2023. PMID: 36696212 Free PMC article.
-
The endothelial cell protein C receptor: cell surface conductor of cytoprotective coagulation factor signaling.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Mar;69(5):717-26. doi: 10.1007/s00018-011-0825-0. Epub 2011 Oct 4. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 21968919 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elevated Angiopoietin-2 Level in Patients With Continuous-Flow Left Ventricular Assist Devices Leads to Altered Angiogenesis and Is Associated With Higher Nonsurgical Bleeding.Circulation. 2016 Jul 12;134(2):141-52. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.019692. Epub 2016 Jun 28. Circulation. 2016. PMID: 27354285 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of anticoagulant and cytoprotective actions of the protein C pathway.J Thromb Haemost. 2013 Jun;11 Suppl 1(0 1):242-53. doi: 10.1111/jth.12247. J Thromb Haemost. 2013. PMID: 23809128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recombinant human activated protein C in the treatment of acute respiratory distress syndrome: a randomized clinical trial.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 14;9(3):e90983. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090983. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24632673 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Mosnier LO, Griffin JH. The cytoprotective protein C pathway. Blood. 2007;109:3161–72. - PubMed
-
- Riewald M, Petrovan RJ, Donner A, Mueller BM, Ruf W. Activation of endothelial cell protease activated receptor 1 by the protein C pathway. Science. 2002;296:1880–2. - PubMed
-
- Finigan JH, Dudek SM, Singleton PA, Chiang ET, Jacobson JR, Camp SM, Ye SQ, Garcia JG. Activated protein C mediates novel lung endothelial barrier enhancement: role of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor transactivation. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:17286–93. - PubMed
-
- Feistritzer C, Riewald M. Endothelial barrier protection by activated protein C through PAR1-dependent sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor-1 crossactivation. Blood. 2005;105:3178–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

