Antifibrotic activity of an inhibitor of histone deacetylases in DOCA-salt hypertensive rats
- PMID: 20180942
- PMCID: PMC2850398
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00637.x
Antifibrotic activity of an inhibitor of histone deacetylases in DOCA-salt hypertensive rats
Abstract
Background and purpose: Histone deacetylases (HDACs) silence genes by deacetylating lysine residues in histones and other proteins. HDAC inhibitors represent a new class of compounds with anti-inflammatory activity. This study investigated whether treatment with a broad spectrum HDAC inhibitor, suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA), would prevent cardiac fibrosis, part of the cardiovascular remodelling in deoxycorticosterone acetate (DOCA)-salt rats.
Experimental approach: Control and DOCA-salt rats were treated with SAHA (25 mg x kg(-1) x day(-1) s.c.) for 32 days. Changes in cardiovascular structure and function were assessed by blood pressure in vivo and in Langendorff perfused hearts, ventricular papillary muscle and in aortic rings in vitro. Left ventricular collagen deposition was assessed by histology.
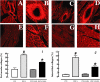
Key results: Administration of SAHA to DOCA-salt rats attenuated the following parameters: the increased concentration of over 20 pro-inflammatory cytokines in plasma, increased inflammatory cell infiltration and interstitial collagen deposition, increased passive diastolic stiffness in perfused hearts, prolongation of action potential duration at 20% and 90% of repolarization in papillary muscle, development of left ventricular hypertrophy, systolic hypertension and changes in vascular dysfunction.
Conclusions and implications: The HDAC inhibitor, SAHA, attenuated the cardiovascular remodelling associated with DOCA-salt hypertensive rats and improved cardiovascular structure and function, especially fibrosis, in the heart and blood vessels, possibly by suppressing inflammation. Control of cardiac histone or non-histone protein acetylation is a potential therapeutic approach to preventing cardiac remodelling, especially cardiac fibrosis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Improved cardiovascular function with aminoguanidine in DOCA-salt hypertensive rats.Br J Pharmacol. 2006 Aug;148(7):902-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706801. Epub 2006 Jun 19. Br J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16783413 Free PMC article.
-
L-carnitine attenuates cardiac remodelling rather than vascular remodelling in deoxycorticosterone acetate-salt hypertensive rats.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2010 Apr;106(4):296-301. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-7843.2009.00480.x. Epub 2009 Nov 11. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2010. PMID: 20041879
-
Reversal of cardiac dysfunction by selective ET-A receptor antagonism.Br J Pharmacol. 2005 Nov;146(6):846-53. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706384. Br J Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 16151437 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting histone deacetylases: development of vorinostat for the treatment of cancer.Epigenomics. 2010 Jun;2(3):457-65. doi: 10.2217/epi.10.20. Epigenomics. 2010. PMID: 22121904 Review.
-
Zn(II)-dependent histone deacetylase inhibitors: suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid and trichostatin A.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009 Apr;41(4):736-9. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2008.05.026. Epub 2008 Aug 3. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 18725319 Review.
Cited by
-
Cardiomyogenic Differentiation Potential of Human Dilated Myocardium-Derived Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells: The Impact of HDAC Inhibitor SAHA and Biomimetic Matrices.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 24;22(23):12702. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312702. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884505 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting inflammation in heart failure with histone deacetylase inhibitors.Mol Med. 2011 May-Jun;17(5-6):434-41. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2011.00022. Epub 2011 Jan 20. Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21267510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles and post-translational regulation of cardiac class IIa histone deacetylase isoforms.J Physiol. 2015 Apr 15;593(8):1785-97. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2014.282442. Epub 2014 Nov 25. J Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25362149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic efficacy of valproic acid in a combined monocrotaline and chronic hypoxia rat model of severe pulmonary hypertension.PLoS One. 2015 Jan 28;10(1):e0117211. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117211. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25629315 Free PMC article.
-
The flavonoid morin restores blood pressure and lipid metabolism in DOCA-salt hypertensive rats.Redox Rep. 2012;17(4):167-75. doi: 10.1179/1351000212Y.0000000015. Epub 2012 Jul 9. Redox Rep. 2012. PMID: 22781105 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adcock IM, Ito K, Barnes PJ. Histone deacetylation: an important mechanism in inflammatory lung diseases. COPD. 2005;2:445–455. - PubMed
-
- Antos CL, McKinsey T, Dreitz M, Hollingsworth LM, Zhang CL, Schreiber K, et al. Dose-dependent blockade to cardiomyocyte hypertrophy by histone deacetylase inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:28930–28937. - PubMed
-
- Bhavsar P, Ahmad T, Adcock IM. The role of histone deacetylases in asthma and allergic diseases. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008;121:580–584. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

