Pyk2 uncouples metabotropic glutamate receptor G protein signaling but facilitates ERK1/2 activation
- PMID: 20180987
- PMCID: PMC2829546
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-6606-3-4
Pyk2 uncouples metabotropic glutamate receptor G protein signaling but facilitates ERK1/2 activation
Abstract
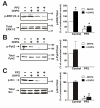
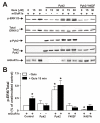
Group I metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) are coupled via Galphaq/11 to the activation of phospholipase Cbeta, which hydrolyzes membrane phospholipids to form inositol 1,4,5 trisphosphate and diacylglycerol. This results in the release of Ca2+ from intracellular stores and the activation of protein kinase C. The activation of Group I mGluRs also results in ERK1/2 phosphorylation. We show here, that the proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 (Pyk2) interacts with both mGluR1 and mGluR5 and is precipitated with both receptors from rat brain. Pyk2 also interacts with GST-fusion proteins corresponding to the second intracellular loop and the distal carboxyl-terminal tail domains of mGluR1a. Pyk2 colocalizes with mGluR1a at the plasma membrane in human embryonic kidney (HEK293) cells and with endogenous mGluR5 in cortical neurons. Pyk2 overexpression in HEK293 results in attenuated basal and agonist-stimulated inositol phosphate formation in mGluR1 expressing cells and involves a mechanism whereby Pyk2 displaces Galphaq/11 from the receptor. The activation of endogenous mGluR1 in primary mouse cortical neuron stimulates ERK1/2 phosphorylation. Treatments that prevent Pyk2 phosphorylation in cortical neurons, and the overexpression of Pyk2 dominant-negative and catalytically inactive Pyk2 mutants in HEK293 cells, prevent ERK1/2 phosphorylation. The Pyk2 mediated activation of ERK1/2 phosphorylation is also Src-, calmodulin- and protein kinase C-dependent. Our data reveal that Pyk2 couples the activation mGluRs to the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway even though it attenuates mGluR1-dependent G protein signaling.
Figures








References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

