Early lactate clearance is associated with biomarkers of inflammation, coagulation, apoptosis, organ dysfunction and mortality in severe sepsis and septic shock
- PMID: 20181046
- PMCID: PMC2837000
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-9255-7-6
Early lactate clearance is associated with biomarkers of inflammation, coagulation, apoptosis, organ dysfunction and mortality in severe sepsis and septic shock
Abstract
Background: Lactate clearance, a surrogate for the magnitude and duration of global tissue hypoxia, is used diagnostically, therapeutically and prognostically. This study examined the association of early lactate clearance with selected inflammatory, coagulation, apoptosis response biomarkers and organ dysfunction scores in severe sepsis and septic shock.
Methods: Measurements of serum arterial lactate, biomarkers (interleukin-1 receptor antagonist, interleukin-6, interleukin-8, interleukin-10, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, intercellular adhesion molecule-1, high mobility group box-1, D-Dimer and caspase-3), and organ dysfunction scores (Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II, Simplified Acute Physiology Score II, Multiple Organ Dysfunction Score, and Sequential Organ Failure Assessment) were obtained in conjunction with a prospective, randomized study examining early goal-directed therapy in severe sepsis and septic shock patients presenting to the emergency department (ED). Lactate clearance was defined as the percent change in lactate levels after six hours from a baseline measurement in the ED.
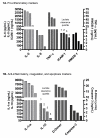
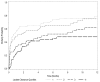
Results: Two-hundred and twenty patients, age 65.0 +/- 17.1 years, were examined, with an overall lactate clearance of 35.5 +/- 43.1% and in-hospital mortality rate of 35.0%. Patients were divided into four quartiles of lactate clearance, -24.3 +/- 42.3, 30.1 +/- 7.5, 53.4 +/- 6.6, and 75.1 +/- 7.1%, respectively (p < 0.01). The mean levels of all biomarkers and organ dysfunction scores over 72 hours were significantly lower with higher lactate clearance quartiles (p < 0.01). There was a significant decreased in-hospital, 28-day, and 60-day mortality in the higher lactate clearance quartiles (p < 0.01).
Conclusions: Early lactate clearance as a surrogate for the resolution of global tissue hypoxia is significantly associated with decreased levels of biomarkers, improvement in organ dysfunction and outcome in severe sepsis and septic shock.
Figures
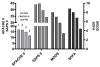
References
-
- Marshall JC, Vincent JL, Fink MP, Cook DJ, Rubenfeld G, Foster D, Fisher CJ Jr, Faist E, Reinhart K. Measures, markers, and mediators: toward a staging system for clinical sepsis. A report of the Fifth Toronto Sepsis Roundtable, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, October 25-26, 2000. Crit Care Med. 2003;31:1560–7. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000065186.67848.3A. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nadiri A, Wolinski MK, Saleh M. The inflammatory caspases: key players in the host response to pathogenic invasion and sepsis. J Immunol. 2006;177:4239–45. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

